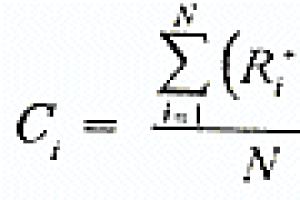Here you can find basic information about pyramids and related formulas and concepts. All of them are studied with a mathematics tutor in preparation for the Unified State Exam.
Consider a plane, a polygon  , lying in it and a point S, not lying in it. Let's connect S to all the vertices of the polygon. The resulting polyhedron is called a pyramid. The segments are called side ribs.
, lying in it and a point S, not lying in it. Let's connect S to all the vertices of the polygon. The resulting polyhedron is called a pyramid. The segments are called side ribs.  The polygon is called the base, and point S is the top of the pyramid. Depending on the number n, the pyramid is called triangular (n=3), quadrangular (n=4), pentagonal (n=5) and so on. An alternative name for a triangular pyramid is tetrahedron. The height of a pyramid is the perpendicular descending from its top to the plane of the base.
The polygon is called the base, and point S is the top of the pyramid. Depending on the number n, the pyramid is called triangular (n=3), quadrangular (n=4), pentagonal (n=5) and so on. An alternative name for a triangular pyramid is tetrahedron. The height of a pyramid is the perpendicular descending from its top to the plane of the base. 
A pyramid is called regular if  a regular polygon, and the base of the pyramid's altitude (the base of the perpendicular) is its center.
a regular polygon, and the base of the pyramid's altitude (the base of the perpendicular) is its center.
Tutor's comment:
Do not confuse the concepts of “regular pyramid” and “regular tetrahedron”. In a regular pyramid, the side edges are not necessarily equal to the edges of the base, but in a regular tetrahedron, all 6 edges are equal. This is his definition. It is easy to prove that the equality implies that the center P of the polygon coincides  with a base height, so a regular tetrahedron is a regular pyramid.
with a base height, so a regular tetrahedron is a regular pyramid.
What is an apothem?
The apothem of a pyramid is the height of its side face. If the pyramid is regular, then all its apothems are equal. The reverse is not true. 
A mathematics tutor about his terminology: 80% of work with pyramids is built through two types of triangles:
1) Containing apothem SK and height SP
2) Containing the lateral edge SA and its projection PA 
To simplify references to these triangles, it is more convenient for a math tutor to call the first of them apothemal, and second costal. Unfortunately, you will not find this terminology in any of the textbooks, and the teacher has to introduce it unilaterally.
Formula for the volume of a pyramid:
1) ![]() , where is the area of the base of the pyramid, and is the height of the pyramid
, where is the area of the base of the pyramid, and is the height of the pyramid
2) , where is the radius of the inscribed sphere, and is the area of the total surface of the pyramid.
3) , where MN is the distance of any two crossing edges, and is the area of the parallelogram formed by the midpoints of the four remaining edges.
Property of the base of the height of a pyramid:
 Point P (see figure) coincides with the center of the inscribed circle at the base of the pyramid if one of the following conditions is met:
Point P (see figure) coincides with the center of the inscribed circle at the base of the pyramid if one of the following conditions is met:
1) All apothems are equal
2) All side faces are equally inclined to the base
3) All apothems are equally inclined to the height of the pyramid
4) The height of the pyramid is equally inclined to all side faces
Math tutor's comment: Please note that all points are united by one common property: one way or another, lateral faces are involved everywhere (apothems are their elements). Therefore, the tutor can offer a less precise, but more convenient for learning, formulation: point P coincides with the center of the inscribed circle, the base of the pyramid, if there is any equal information about its lateral faces. To prove it, it is enough to show that all apothem triangles are equal.
 Point P coincides with the center of a circle circumscribed near the base of the pyramid if one of three conditions is true:
Point P coincides with the center of a circle circumscribed near the base of the pyramid if one of three conditions is true:
1) All side edges are equal
2) All side ribs are equally inclined to the base
3) All side ribs are equally inclined to the height
Definition. Side edge- this is a triangle in which one angle lies at the top of the pyramid, and the opposite side coincides with the side of the base (polygon).
Definition. Side ribs- these are the common sides of the side faces. A pyramid has as many edges as the angles of a polygon.
Definition. Pyramid height- this is a perpendicular lowered from the top to the base of the pyramid.
Definition. Apothem- this is a perpendicular to the side face of the pyramid, lowered from the top of the pyramid to the side of the base.
Definition. Diagonal section- this is a section of a pyramid by a plane passing through the top of the pyramid and the diagonal of the base.
Definition. Correct pyramid is a pyramid in which the base is a regular polygon, and the height descends to the center of the base.
Volume and surface area of the pyramid
Formula. Volume of the pyramid through base area and height:
Properties of the pyramid
If all the side edges are equal, then a circle can be drawn around the base of the pyramid, and the center of the base coincides with the center of the circle. Also, a perpendicular dropped from the top passes through the center of the base (circle).
If all the side edges are equal, then they are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angles.
The lateral edges are equal when they form equal angles with the plane of the base or if a circle can be described around the base of the pyramid.
If the side faces are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angle, then a circle can be inscribed into the base of the pyramid, and the top of the pyramid is projected at its center.
If the side faces are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angle, then the apothems of the side faces are equal.
Properties of a regular pyramid
1. The top of the pyramid is equidistant from all corners of the base.
2. All side edges are equal.
3. All side ribs are inclined at equal angles to the base.
4. The apothems of all lateral faces are equal.
5. The areas of all side faces are equal.
6. All faces have the same dihedral (flat) angles.
7. A sphere can be described around the pyramid. The center of the circumscribed sphere will be the intersection point of the perpendiculars that pass through the middle of the edges.
8. You can fit a sphere into a pyramid. The center of the inscribed sphere will be the point of intersection of the bisectors emanating from the angle between the edge and the base.
9. If the center of the inscribed sphere coincides with the center of the circumscribed sphere, then the sum of the plane angles at the vertex is equal to π or vice versa, one angle is equal to π/n, where n is the number of angles at the base of the pyramid.
The connection between the pyramid and the sphere

A sphere can be described around a pyramid when at the base of the pyramid there is a polyhedron around which a circle can be described (a necessary and sufficient condition). The center of the sphere will be the intersection point of planes passing perpendicularly through the midpoints of the side edges of the pyramid.
It is always possible to describe a sphere around any triangular or regular pyramid.

A sphere can be inscribed in a pyramid if the bisector planes of the internal dihedral angles of the pyramid intersect at one point (a necessary and sufficient condition). This point will be the center of the sphere.
Connection of a pyramid with a cone
A cone is said to be inscribed in a pyramid if their vertices coincide and the base of the cone is inscribed in the base of the pyramid.
A cone can be inscribed in a pyramid if the apothems of the pyramid are equal to each other.
A cone is said to be circumscribed around a pyramid if their vertices coincide and the base of the cone is circumscribed around the base of the pyramid.
A cone can be described around a pyramid if all the lateral edges of the pyramid are equal to each other.
Relationship between a pyramid and a cylinder
A pyramid is called inscribed in a cylinder if the top of the pyramid lies on one base of the cylinder, and the base of the pyramid is inscribed in another base of the cylinder.
A cylinder can be described around a pyramid if a circle can be described around the base of the pyramid.


A tetrahedron has four faces and four vertices and six edges, where any two edges do not have common vertices but do not touch.
Each vertex consists of three faces and edges that form triangular angle.
The segment connecting the vertex of a tetrahedron with the center of the opposite face is called median of the tetrahedron(GM).
Bimedian called a segment connecting the midpoints of opposite edges that do not touch (KL).
All bimedians and medians of a tetrahedron intersect at one point (S). In this case, the bimedians are divided in half, and the medians are divided in a ratio of 3:1 starting from the top.


Definition. Acute angled pyramid- a pyramid in which the apothem is more than half the length of the side of the base.
Definition. Obtuse pyramid- a pyramid in which the apothem is less than half the length of the side of the base.
Definition. Regular tetrahedron- a tetrahedron in which all four faces are equilateral triangles. It is one of the five regular polygons. In a regular tetrahedron, all dihedral angles (between faces) and trihedral angles (at the vertex) are equal.
Definition. Rectangular tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron in which there is a right angle between three edges at the apex (the edges are perpendicular). Three faces form rectangular triangular angle and the faces are right triangles, and the base is an arbitrary triangle. The apothem of any face is equal to half the side of the base on which the apothem falls.
Definition. Isohedral tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron whose side faces are equal to each other, and the base is a regular triangle. Such a tetrahedron has faces that are isosceles triangles.
Definition. Orthocentric tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron in which all the heights (perpendiculars) that are lowered from the top to the opposite face intersect at one point.
Definition. Star pyramid called a polyhedron whose base is a star.

Maintaining your privacy is important to us. For this reason, we have developed a Privacy Policy that describes how we use and store your information. Please review our privacy practices and let us know if you have any questions.
Collection and use of personal information
Personal information refers to data that can be used to identify or contact a specific person.
You may be asked to provide your personal information at any time when you contact us.
Below are some examples of the types of personal information we may collect and how we may use such information.
What personal information do we collect:
- When you submit an application on the site, we may collect various information, including your name, telephone number, email address, etc.
How we use your personal information:
- The personal information we collect allows us to contact you with unique offers, promotions and other events and upcoming events.
- From time to time, we may use your personal information to send important notices and communications.
- We may also use personal information for internal purposes, such as conducting audits, data analysis and various research in order to improve the services we provide and provide you with recommendations regarding our services.
- If you participate in a prize draw, contest or similar promotion, we may use the information you provide to administer such programs.
Disclosure of information to third parties
We do not disclose the information received from you to third parties.
Exceptions:
- If necessary - in accordance with the law, judicial procedure, in legal proceedings, and/or on the basis of public requests or requests from government authorities in the territory of the Russian Federation - to disclose your personal information. We may also disclose information about you if we determine that such disclosure is necessary or appropriate for security, law enforcement, or other public importance purposes.
- In the event of a reorganization, merger, or sale, we may transfer the personal information we collect to the applicable successor third party.
Protection of personal information
We take precautions - including administrative, technical and physical - to protect your personal information from loss, theft, and misuse, as well as unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration and destruction.
Respecting your privacy at the company level
To ensure that your personal information is secure, we communicate privacy and security standards to our employees and strictly enforce privacy practices.
This video tutorial will help users get an idea of the Pyramid theme. Correct pyramid. In this lesson we will get acquainted with the concept of a pyramid and give it a definition. Let's consider what a regular pyramid is and what properties it has. Then we prove the theorem about the lateral surface of a regular pyramid.
In this lesson we will get acquainted with the concept of a pyramid and give it a definition.
Consider a polygon A 1 A 2...A n, which lies in the α plane, and the point P, which does not lie in the α plane (Fig. 1). Let's connect the dots P with peaks A 1, A 2, A 3, … A n. We get n triangles: A 1 A 2 R, A 2 A 3 R and so on.
Definition. Polyhedron RA 1 A 2 ...A n, made up of n-square A 1 A 2...A n And n triangles RA 1 A 2, RA 2 A 3 …RA n A n-1 is called n-coal pyramid. Rice. 1.
Rice. 1
Consider a quadrangular pyramid PABCD(Fig. 2).
R- the top of the pyramid.
ABCD- the base of the pyramid.
RA- side rib.
AB- base rib.
From point R let's drop the perpendicular RN to the base plane ABCD. The perpendicular drawn is the height of the pyramid.

Rice. 2
The full surface of the pyramid consists of the lateral surface, that is, the area of all lateral faces, and the area of the base:
S full = S side + S main
A pyramid is called correct if:
- its base is a regular polygon;
- the segment connecting the top of the pyramid to the center of the base is its height.
Explanation using the example of a regular quadrangular pyramid
Consider a regular quadrangular pyramid PABCD(Fig. 3).
R- the top of the pyramid. Base of the pyramid ABCD- a regular quadrilateral, that is, a square. Dot ABOUT, the point of intersection of the diagonals, is the center of the square. Means, RO is the height of the pyramid.

Rice. 3
Explanation: in the correct n In a triangle, the center of the inscribed circle and the center of the circumcircle coincide. This center is called the center of the polygon. Sometimes they say that the vertex is projected into the center.
The height of the side face of a regular pyramid drawn from its vertex is called apothem and is designated h a.
1. all lateral edges of a regular pyramid are equal;
2. The side faces are equal isosceles triangles.
We will give a proof of these properties using the example of a regular quadrangular pyramid.
Given: PABCD- regular quadrangular pyramid,
ABCD- square,
RO- height of the pyramid.
Prove:
1. RA = PB = RS = PD
2.∆ABP = ∆BCP =∆CDP =∆DAP See Fig. 4.

Rice. 4
Proof.
RO- height of the pyramid. That is, straight RO perpendicular to the plane ABC, and therefore direct JSC, VO, SO And DO lying in it. So triangles ROA, ROV, ROS, ROD- rectangular.
Consider a square ABCD. From the properties of a square it follows that AO = VO = CO = DO.
Then the right triangles ROA, ROV, ROS, ROD leg RO- general and legs JSC, VO, SO And DO are equal, which means that these triangles are equal on two sides. From the equality of triangles follows the equality of segments, RA = PB = RS = PD. Point 1 has been proven.
Segments AB And Sun are equal because they are sides of the same square, RA = PB = RS. So triangles AVR And VSR - isosceles and equal on three sides.
In a similar way we find that triangles ABP, VCP, CDP, DAP are isosceles and equal, as required to be proved in paragraph 2.
The area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid is equal to half the product of the perimeter of the base and the apothem:
![]()
To prove this, let’s choose a regular triangular pyramid.
Given: RAVS- regular triangular pyramid.
AB = BC = AC.
RO- height.
Prove: ![]() . See Fig. 5.
. See Fig. 5.

Rice. 5
Proof.
RAVS- regular triangular pyramid. That is AB= AC = BC. Let ABOUT- center of the triangle ABC, Then RO is the height of the pyramid. At the base of the pyramid lies an equilateral triangle ABC. notice, that ![]() .
.
Triangles RAV, RVS, RSA- equal isosceles triangles (by property). A triangular pyramid has three side faces: RAV, RVS, RSA. This means that the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid is:
S side = 3S RAW
The theorem has been proven.
The radius of a circle inscribed at the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid is 3 m, the height of the pyramid is 4 m. Find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Given: regular quadrangular pyramid ABCD,
ABCD- square,
r= 3 m,
RO- height of the pyramid,
RO= 4 m.
Find: S side. See Fig. 6.

Rice. 6
Solution.
According to the proven theorem, .
Let's first find the side of the base AB. We know that the radius of a circle inscribed at the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid is 3 m.
Then, m.
Find the perimeter of the square ABCD with a side of 6 m:
Consider a triangle BCD. Let M- middle of the side DC. Because ABOUT- middle BD, That ![]() (m).
(m).
Triangle DPC- isosceles. M- middle DC. That is, RM- median, and therefore height in the triangle DPC. Then RM- apothem of the pyramid.
RO- height of the pyramid. Then, straight RO perpendicular to the plane ABC, and therefore direct OM, lying in it. Let's find the apothem RM from a right triangle ROM.
Now we can find the lateral surface of the pyramid:
Answer: 60 m2.
The radius of the circle circumscribed around the base of a regular triangular pyramid is equal to m. The lateral surface area is 18 m 2. Find the length of the apothem.
Given: ABCP- regular triangular pyramid,
AB = BC = SA,
R= m,
S side = 18 m2.
Find: . See Fig. 7.

Rice. 7
Solution.
In a right triangle ABC The radius of the circumscribed circle is given. Let's find a side AB this triangle using the law of sines.
![]()
Knowing the side of a regular triangle (m), we find its perimeter.
By the theorem on the lateral surface area of a regular pyramid, where h a- apothem of the pyramid. Then:
![]()
Answer: 4 m.
So, we looked at what a pyramid is, what a regular pyramid is, and we proved the theorem about the lateral surface of a regular pyramid. In the next lesson we will get acquainted with the truncated pyramid.
Bibliography
- Geometry. Grades 10-11: textbook for students of general education institutions (basic and specialized levels) / I. M. Smirnova, V. A. Smirnov. - 5th ed., rev. and additional - M.: Mnemosyne, 2008. - 288 p.: ill.
- Geometry. Grades 10-11: Textbook for general education institutions / Sharygin I. F. - M.: Bustard, 1999. - 208 pp.: ill.
- Geometry. Grade 10: Textbook for general education institutions with in-depth and specialized study of mathematics /E. V. Potoskuev, L. I. Zvalich. - 6th ed., stereotype. - M.: Bustard, 008. - 233 p.: ill.
- Internet portal "Yaklass" ()
- Internet portal “Festival of pedagogical ideas “First of September” ()
- Internet portal “Slideshare.net” ()
Homework
- Can a regular polygon be the base of an irregular pyramid?
- Prove that disjoint edges of a regular pyramid are perpendicular.
- Find the value of the dihedral angle at the side of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid if the apothem of the pyramid is equal to the side of its base.
- RAVS- regular triangular pyramid. Construct the linear angle of the dihedral angle at the base of the pyramid.
Definition 1. A pyramid is called regular if its base is a regular polygon, and the vertex of such a pyramid is projected into the center of its base.
Definition 2. A pyramid is called regular if its base is a regular polygon and its height passes through the center of the base.
Elements of a regular pyramid
- The height of a side face drawn from its vertex is called apothem. In the figure it is designated as segment ON
- A point connecting the lateral edges and not lying in the plane of the base is called the top of the pyramid(ABOUT)
- Triangles that have a common side with the base and one of the vertices coinciding with the vertex are called side faces(AOD, DOC, COB, AOB)
- The perpendicular segment drawn through the top of the pyramid to the plane of its base is called pyramid height(OK)
- Diagonal section of a pyramid- this is the section passing through the apex and diagonal of the base (AOC, BOD)
- A polygon that does not have a vertex of the pyramid is called base of the pyramid(ABCD)
If at the base regular pyramid lies a triangle, quadrilateral, etc. then it's called regular triangular , quadrangular etc.
A triangular pyramid is a tetrahedron - a tetrahedron.
Properties of a regular pyramid
To solve problems, it is necessary to know the properties of individual elements, which are usually omitted in the condition, since it is believed that the student should know this from the beginning.
- side ribs are equal between themselves
- apothems are equal
- side faces are equal among themselves (in this case, their areas, sides and bases are respectively equal), that is, they are equal triangles
- all lateral faces are equal isosceles triangles
- in any regular pyramid you can both fit and describe a sphere around it
- if the centers of the inscribed and circumscribed spheres coincide, then the sum of the plane angles at the top of the pyramid is equal to π, and each of them is π/n, respectively, where n is the number of sides of the base polygon
- The area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid is equal to half the product of the perimeter of the base and the apothem
- a circle can be circumscribed around the base of a regular pyramid (see also circumscribed circle radius of a triangle)
- all lateral faces form equal angles with the plane of the base of a regular pyramid
- all heights of the side faces are equal to each other
Instructions for solving problems. The properties listed above should help in a practical solution. If you need to find the angles of inclination of the faces, their surface, etc., then the general technique comes down to dividing the entire volumetric figure into separate flat figures and using their properties to find individual elements of the pyramid, since many elements are common to several figures.
It is necessary to break the entire three-dimensional figure into individual elements - triangles, squares, segments. Next, apply knowledge from the planimetry course to individual elements, which greatly simplifies finding the answer.
Formulas for a regular pyramid
Formulas for finding volume and lateral surface area:

Designations:
V - volume of the pyramid
S - base area
h - height of the pyramid
Sb - lateral surface area
a - apothem (not to be confused with α)
P - base perimeter
n - number of sides of the base
b - side rib length
α - flat angle at the top of the pyramid
This formula for finding volume can be applied only For correct pyramid:
 , Where
, Where
V - volume of a regular pyramid
h - height of a regular pyramid
n is the number of sides of a regular polygon, which is the base of a regular pyramid
a - side length of a regular polygon
Regular truncated pyramid
If we draw a section parallel to the base of the pyramid, then the body enclosed between these planes and the lateral surface is called truncated pyramid. This section for a truncated pyramid is one of its bases.
The height of the side face (which is an isosceles trapezoid) is called - apothem of a regular truncated pyramid.
A truncated pyramid is called regular if the pyramid from which it was derived is regular.
- The distance between the bases of a truncated pyramid is called height of a truncated pyramid
- All faces of a regular truncated pyramid are equilateral (isosceles) trapezoids
Notes
See also: special cases (formulas) for a regular pyramid:
How to use the theoretical materials provided here to solve your problem: