§ 12. Oxoacids of E(VI) chalcogens: preparation, structure, properties.
Oxoacids chalcogens(VI) H 2 SO 4 , H 2 SeO 4 and H 6 TeO 6 are synthesized by oxidation of their dioxides (or corresponding acids):
H 2 SeO 3 + H 2 O 2 H 2 SeO 4 + H 2 O
5TeO 2 + 2KMnO 4 + 6HNO 3 + 12 H 2 O 5H 6 TeO 6 + 2KNO 3 + 2Mn(NO 3) 2,
as well as the oxidation of simple substances with strong oxidizing agents:
5Te + 6HClO 3 + 12H 2 O 5H 6 TeO 6 + 3Cl 2,
or exchange reactions:
BaTeO 4 + H 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O H 6 TeO 6 + BaSO 4 .
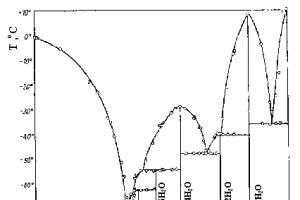
In the H 2 SO 4 molecule, sulfur is tetrahedrally surrounded by two hydroxyl (OH) groups and two oxygen atoms. The bond lengths (the S-OH distance is 1.54, and the S-O distance is 1.43) in the H 2 SO 4 molecule are such that the S-O bonds can be considered double, and the S-OH bonds can be considered single. Colorless, ice-like crystals of H 2 SO 4 have a layered structure in which each H 2 SO 4 molecule is connected to four neighboring molecules by strong hydrogen bonds, forming a single spatial framework. At a temperature of 10.48 o C, H 2 SO 4 melts to form a heavy (d = 1.838 g/ml at 15 o C) oily liquid, boiling at 280 o C. Liquid H 2 SO 4 has a structure almost the same as that of solid, only the integrity of the spatial framework is broken, and it can be represented as a collection of microcrystals that are constantly changing their shape. H 2 SO 4 mixes with water in any ratio, which is accompanied by the formation of H 2 SO 4 hydrates. nH2O (Fig. 8). The heat of hydration is so great that the mixture may even boil.

Fig.8. T-x diagram of the H 2 O-H 2 SO 4 system.
Liquid H 2 SO 4 is surprisingly similar to water with all its structural features and anomalies. Here there is the same system of strong hydrogen bonds as in water, almost the same strong spatial framework, the same abnormally high viscosity, surface tension, melting and boiling points. The dielectric constant of H 2 SO 4 is high (100). For this reason, the intrinsic dissociation ( autoionization) for sulfuric acid is noticeably greater than for water: 2H 2 SO 4 H 3 SO 4 + + HSO 4-, K = 2.7 . 10 -4 .
Due to its high polarity, the H-O bond is easily broken, and the removal of a proton requires less energy than that of water. For this reason, the acidic properties of H 2 SO 4 are strongly expressed and, when dissolved in anhydrous H 2 SO 4, most compounds traditionally considered acids (CH 3 COOH, HNO 3, H 3 PO 4, etc.) behave like bases, entering in the neutralization reaction and increasing the concentration of anions:
H 2 O + H 2 SO 4 H 3 O + + ,
base
CH 3 COOH + H 2 SO 4 CH 3 C(OH) 2 + + ,
base
HNO 3 + 2 H 2 SO 4 NO 2 + + H 3 O + +2,
base
Only a few compounds (HClO 4, FSO 3 H) when dissolved in H 2 SO 4 behave like weak acids, that is, their proton is removed more easily than that of H 2 SO 4, which leads to an increase in the concentration of the solvated proton, for example,
HSO 3 F + H 2 SO 4 + SO 3 F-.
Some properties of chalcogen oxoacids (VI) are given in Table 9.
Table 9. Properties of oxoacids of E(VI) chalcogens.
H2TeO4. 2H 2 O=H 6 TeO 6 |
|||
| pK 1: H 2 EO 4 =
H + +NEO 4 - pK 2: |
|||
| E o, B; pH = 0: | |||
| E o, B; pH = 14: |
Sulfuric and selenic acids are strong dibasic acids and are similar in structure and properties to each other. Their dissociation constants in aqueous solutions are of the same order (K 2 for and are equal to 1.2.10 -2 and 2.19.10 -2, respectively), selenates are isomorphic with sulfates, forming, for example, alum of the composition МAl(SeO 4) 3 . 12H 2 O, where M - heavy alkali metal .
Structure orthotelluric acid H 6 TeO 6 differs in structure from sulfuric and selenic acids (compare with the oxygen acids of the halogens HClO 4 , HBrO 4 and H 5 IO 6 ). The crystal structure of solid H 6 TeO 6 (mp 136 o C) is built from molecules of regular octahedral shape, which retain their shape in solutions. Tellurates are not isomorphic with sulfates and selenates. Orthotelluric acid is titrated with alkali as a monobasic acid to form salts M I TeO(OH) 5; it is weaker than carbonic acid. The products of complete (Ag 6 TeO 6, Na 6 TeO 6) and partial (NaH 5 TeO 6, Na 2 H 4 TeO 6, Na 4 H 2 TeO 6) products were obtained. replacement of protons with metal ions.
Selenic acid a stronger oxidizing agent than H 2 SO 4 and H 6 TeO 6 (Table 9). It dissolves Cu and even Au without heating: 2Au + 6H 2 SeO 4 Au 2 (SeO 4) 3 + 3 H 2 SeO 3 + 2H 2 O, oxidizes halide ions, except fluoride, to free halogens, and under its influence the fiber ignites. Orthotelluric acid is also a stronger oxidizing agent than sulfuric acid. The most common reduction product is H 2 SeO 4 and H 6 TeO 6 are simple substances.
Sulfuric acid has strong oxidizing properties only in concentrated form and when heated:
Cu + 2 H 2 SO 4 CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O.
The products of its reduction, depending on the reaction conditions, can be SO 2 (with an excess of H 2 SO 4), H 2 S, S, polythionates (with a lack of H 2 SO 4).
In the - - H 5 Te series, an anomaly is observed in the sequence of changes in thermodynamic stability and oxidizing ability: selenic acid and its salts are thermodynamically less stable and stronger oxidizing agents than the corresponding acids and salts S(VI) and Te(VI). Slope of the line connecting volt-equivalent pairs ![]() , greater than the slope of the corresponding lines for H 6 TeO 6 - H 2 TeO 3 and - H 2 SO 3 (Fig. 7). The greater potential of the pair / compared to the pairs H 6 TeO 6 / H 2 TeO 3 and / H 2 SO 3 leads to the fact that H 2 SeO 4, for example, releases chlorine from concentrated HCl: H 2 SeO 4 + 2HCl = Cl 2 + H 2 SeO 3 + H 2 O. Similar non-monotonic changes in the properties of elements and their compounds, in particular oxoacids, are also observed for other elements of the 4th period, for example,
, greater than the slope of the corresponding lines for H 6 TeO 6 - H 2 TeO 3 and - H 2 SO 3 (Fig. 7). The greater potential of the pair / compared to the pairs H 6 TeO 6 / H 2 TeO 3 and / H 2 SO 3 leads to the fact that H 2 SeO 4, for example, releases chlorine from concentrated HCl: H 2 SeO 4 + 2HCl = Cl 2 + H 2 SeO 3 + H 2 O. Similar non-monotonic changes in the properties of elements and their compounds, in particular oxoacids, are also observed for other elements of the 4th period, for example, ![]() , and are sometimes called secondary periodicity. It can be assumed that the anomalies under consideration are associated with a decrease in the strength of the Se-O bond compared to the S-O bond. In turn, this is caused by an increase in the size and energies of the 4s and 4p orbitals of the selenium atom compared to the size and energies of the 2s and 2p -oxygen orbitals, and therefore with a decrease in interaction (overlap) 4s-,
4p -
orbitals of selenium and 2s, 2p-orbitals of oxygen (the energies of 2s-, 2p-, 3s-, 3p-, 4s- and 4p-atomic orbitals are - 32.4, - 15.9, - 20.7, - 12.0, - 17.6 and - 9.1 eV, respectively). Increased stability and decreased oxidative capacity of oxo compounds upon transition from Se(VI) to Te(VI) )
due to structural features and an increase in the strength of the Te-O bond in octahedral TeO 6 ions compared to the Se-O bond in tetrahedra. The tellurium atom has a larger radius than the selenium atom and is characterized by a coordination number of 6. An increase in the number of coordinated oxygen atoms leads to an increase in the number of electrons in the bonding molecular orbitals and, accordingly, to an increase in bond strength.
, and are sometimes called secondary periodicity. It can be assumed that the anomalies under consideration are associated with a decrease in the strength of the Se-O bond compared to the S-O bond. In turn, this is caused by an increase in the size and energies of the 4s and 4p orbitals of the selenium atom compared to the size and energies of the 2s and 2p -oxygen orbitals, and therefore with a decrease in interaction (overlap) 4s-,
4p -
orbitals of selenium and 2s, 2p-orbitals of oxygen (the energies of 2s-, 2p-, 3s-, 3p-, 4s- and 4p-atomic orbitals are - 32.4, - 15.9, - 20.7, - 12.0, - 17.6 and - 9.1 eV, respectively). Increased stability and decreased oxidative capacity of oxo compounds upon transition from Se(VI) to Te(VI) )
due to structural features and an increase in the strength of the Te-O bond in octahedral TeO 6 ions compared to the Se-O bond in tetrahedra. The tellurium atom has a larger radius than the selenium atom and is characterized by a coordination number of 6. An increase in the number of coordinated oxygen atoms leads to an increase in the number of electrons in the bonding molecular orbitals and, accordingly, to an increase in bond strength.
Receipt
- Reaction of selenium(VI) oxide with water:
texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(SeO_3 + H_2O \longrightarrow H_2SeO_4)
- Interaction of selenium with chlorine or bromine water:
Unable to parse expression (Executable file texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(Se + 3 Cl_2 + 4 H_2O \longrightarrow H_2SeO_4 + 6 HCl)
Unable to parse expression (Executable file texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(Se + 3 Br_2 + 4 H_2O \longrightarrow H_2SeO_4 + 6 HBr)
- Interaction of selenous acid or selenium(IV) oxide with hydrogen peroxide:
Unable to parse expression (Executable file texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(SeO_2 + H_2O_2 \longrightarrow H_2SeO_4 )
Unable to parse expression (Executable file texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(H_2SeO_3 + H_2O_2 \longrightarrow H_2SeO_4 + H_2O )
Chemical properties
- Change in color of acid-base indicators
- Hot, concentrated selenic acid can dissolve gold, forming a red-yellow solution of gold(III) selenate:
Unable to parse expression (Executable file texvc not found; See math/README for setup help.): \mathsf(2Au + 6 H_2SeO_4 \longrightarrow Au_2(SeO_4)_3 + 3 H_2SeO_3 + 3 H_2O)
To obtain the anhydrous acid in a crystalline solid state, the resulting solution is evaporated at temperatures below 140 °C (413 K, 284 °F) in vacuum.
Concentrated solutions of this viscous acid. Crystalline mono- and dihydrates are known. The monohydrate melts at 26 °C, the dihydrate at −51.7 °C.
Selenates
Salts of selenic acid are called selenates:
- Ammonium selenate - (NH 4) 2 SeO 4
- Gold(III) selenate - Au 2 (SeO 4) 3
- Sodium selenate - Na 2 SeO 4
Application
Selenic acid is used mainly for the production of selenates.
Write a review about the article "Selenic acid"
Notes
| Chemical vessels | This is a draft article about inorganic matter. You can help the project by adding to it. |
Excerpt characterizing selenic acid
Apparently Christina had similar thoughts, because she suddenly asked me for the first time:– Please do something!
I immediately answered her: “Of course!” And I thought to myself: “If only I knew what!!!”... But I had to act, and I decided that I would try until I achieve something - or he will finally hear me, or (in the worst case) he will be thrown out the door again.
- So are you going to talk or not? – I asked deliberately angrily. “I don’t have time for you, and I’m here only because this wonderful little man is with me - your daughter!”
The man suddenly plopped down in a nearby chair and, clasping his head in his hands, began to sob... This went on for quite a long time, and it was clear that he, like most men, did not know how to cry at all. His tears were stingy and heavy, and they apparently were very, very difficult for him. It was only then that I truly understood for the first time what the expression “man’s tears” means...
I sat down on the edge of some bedside table and watched in confusion this stream of other people’s tears, having absolutely no idea what to do next?..
- Mom, mommy, why are such monsters walking here? – a frightened voice asked quietly.
And only then did I notice very strange creatures that were literally “in heaps” hovering around the drunken Arthur...
My hair started to move - these were real “monsters” from children’s fairy tales, only here for some reason they even seemed very, very real... They looked like evil spirits released from a jug, which somehow managed to “attach” directly to the poor man’s breasts, and, hanging on him in clusters, with great pleasure “devoured” his almost exhausted vitality...
I felt that Vesta was scared to the point of a puppy squeal, but she was trying her best not to show it. The poor thing watched in horror as these terrible “monsters” happily and mercilessly “ate” her beloved dad right in front of her eyes... I couldn’t figure out what to do, but I knew that I had to act quickly. Having quickly looked around and not finding anything better, I grabbed a pile of dirty plates and threw them onto the floor with all my might... Arthur jumped in his chair in surprise and stared at me with crazy eyes.
- There’s no point in getting soggy! – I shouted, “look what “friends” you brought into your house!
I wasn’t sure whether he would see the same thing that we saw, but this was my only hope to somehow “come to his senses” and thus make him sober up at least a little.
By the way his eyes suddenly went up to his forehead, it turned out that he saw... In horror, he flinched into the corner, he could not take his eyes off his “cute” guests and, unable to utter a word, he only pointed at them with a trembling hand. He was shaking slightly, and I realized that if nothing was done, the poor man would have a real nervous attack.
I tried to mentally turn to these strange monstrous creatures, but nothing useful came of it; they only “growled” ominously, swatting me away with their clawed paws, and without turning around, they sent a very painful energy blow straight into my chest. And then, one of them “came unstuck” from Arthur and, having his eye on what he thought was the easiest prey, jumped straight at Vesta... The girl screamed wildly in surprise, but - we must pay tribute to her courage - she immediately began to fight back, which was strength Both of them, he and she, were the same incorporeal entities, so they “understood” each other perfectly and could freely inflict energy blows on each other. And you should have seen with what passion this fearless little girl rushed into battle!.. From the poor cowering “monster” only sparks rained down from her stormy blows, and we, the three of us watching, to our shame, were so dumbfounded that we did not immediately react, so that although I wish I could help her somehow. And just at the same moment, Vesta began to look like a completely squeezed out golden lump and, becoming completely transparent, disappeared somewhere. I realized that she had given all her childhood strength, trying to defend herself, and now she didn’t have enough of it to simply maintain contact with us... Christina looked around in confusion - apparently her daughter did not have the habit of simply disappearing, leaving her alone. I also looked around and then... I saw the most shocked face that I had ever seen in my life, both then and all the subsequent many years... Arthur stood in real shock and looked straight at his wife!.. Apparently too much alcohol , enormous stress, and all subsequent emotions, for a moment opened the “door” between our different worlds and he saw his deceased Christina, as beautiful and as “real” as he had always known her... No words would have been possible describe the expressions in their eyes!.. They did not speak, although, as I understood, Arthur most likely could hear her. I think at that moment he simply could not speak, but in his eyes there was everything - and the wild pain that had been choking him for so long; and boundless happiness that stunned him with its surprise; and prayer, and so much more that there would be no words to try to tell it all!..
Selenium was discovered in 1817 by Jens Jakob Berzelius. Berzelius's own story about how this discovery happened has been preserved: “I investigated, in collaboration with Gottlieb Hahn, the method used for the production of sulfuric acid in Gripsholm. We discovered a precipitate in sulfuric acid, partly red, partly light brown. ... Curiosity , prompted by the hope of discovering a new rare metal in this brown sediment, led me to investigate the sediment... I found that the mass (that is, the sediment) contained a hitherto unknown metal, very similar in its properties to tellurium. In accordance with this analogy I named the new body selenium (Selenium) from the Greek selhnh(moon), since tellurium is named after Tellus - our planet."
Being in nature, receiving:
The selenium content in the earth's crust is about 500 mg/t. Selenium forms 37 minerals, among which the first to be noted are ashavalite FeSe, clausthalite PbSe, timannite HgSe, guanajuatite Bi 2 (Se,S) 3, hastite CoSe 2, platinite PbBi 2 (S,Se) 3. Native selenium is occasionally found. Sulfide deposits are of major industrial importance for selenium. The selenium content in sulfides ranges from 7 to 110 g/t. The concentration of selenium in sea water is 4*10 -4 mg/l.
Selenium is obtained from waste from sulfuric acid and pulp and paper production, and also significant amounts are obtained from sludge from copper electrolyte production, in which selenium is present in the form of silver selenide. Several methods are used to obtain selenium from sludge: oxidative roasting with sublimation of SeO 2 ; oxidative sintering with soda, conversion of the resulting mixture of selenium compounds to Se(IV) compounds and their reduction to elemental selenium by the action of SO 2.
Physical properties:
The diversity of the molecular structure determines the existence of selenium in different allotropic modifications: amorphous (powdery, colloidal, glassy) and crystalline (monoclinic, a- And b-shapes and hexagonal g-form). Amorphous (red) powdered and colloidal selenium is obtained by reduction from a solution of selenous acid by rapid cooling of selenium vapor. Glassy (black) selenium is obtained by heating any modification of selenium above 220°C, followed by rapid cooling. It has a glassy luster and is fragile. Thermodynamically, hexagonal (gray) selenium is the most stable. It is obtained from other forms of selenium by heating until melting, slowly cooling to 180-210°C and holding at this temperature. Its lattice is built from parallel spiral chains of atoms.
Chemical properties:
At ordinary temperatures, selenium is resistant to oxygen, water and dilute acids. When heated, selenium reacts with all metals, forming selenides. In oxygen, with additional heating, it slowly burns with a blue flame, turning into dioxide SeO 2.
It reacts with halogens, with the exception of iodine, at room temperature to form the compounds SeF 6, SeF 4, SeCl 4, Se 2 Cl 2, SeBr 4, etc. With chlorine or bromine water, selenium reacts according to the equation:
Se + 3Br 2 + 4H 2 O = H 2 SeO 4 + 6 HBr
Hydrogen reacts with selenium at t >200°C, giving H 2 Se.
In conc. H 2 SO 4 in the cold, selenium dissolves, giving a green solution containing polymer cations Se 8 2+.
With water when heated and finally. In alkali solutions, selenium disproportionates:
3Se + 3H 2 O = 2H 2 Se + H 2 SeO 3 and 3Se + 6KOH = K 2 SeO 3 + 2K 2 Se + 3H 2 O
forming selenium(-2) and selenium(+4) compounds.
Similarly to sulfur, selenium dissolves when heated in solutions of Na 2 SO 3 or KCN, forming, respectively, Na 2 SSeO 3 (an analogue of thiosulfate) or KCNSe (an analogue of thiosulfate).
The most important connections:
The most typical oxidation states for selenium are -2, +4, +6.
Selenium(IV) oxide SeO 2- white shiny crystals with a polymer molecule (SeOsub>2)sub>n, m.p. 350°C. The vapors are yellowish-green in color and have the smell of rotten radish. Easily dissolves in water to form H 2 SeO 3 .
Selenous acid, H 2 SeO 3- white rhombic crystals. Highly hygroscopic. Highly soluble in water. Unstable, when heated above 70°C it decomposes into water and selenium(IV) oxide. Salts are selenites.
Sodium selenite, Na 2 SeO 3– colorless crystals, m.p. 711°C. Hygroscopic, highly soluble in water. When heated in an inert atmosphere, it decomposes into oxides. When heated in air, it oxidizes to selenate: 2Na 2 SeO 3 + O 2 = 2Na 2 SeO 4
Selenium(VI) oxide SeO 3- - colorless crystals, m.p. 121°C. It is hygroscopic, reacts with water with large heat release and the formation of H 2 SeO 4. Strong oxidizing agent, reacts violently with organic substances
Selenic acid, H 2 SeO 4- a colorless crystalline substance, highly soluble in water. It is toxic, hygroscopic, and a strong oxidizing agent. Selenic acid is one of the few compounds that, when heated, dissolves gold, forming a red-yellow solution of gold(III) selenate.
2Au + 6H 2 SeO 4 = Au 2 (SeO 4) 3 + 3H 2 SeO 3 + 3H 2 O
Selenates- salts of selenic acid. Sodium selenate Na 2 SeO 4 - crystals of orthorhombic system; tmelt 730 °C. Obtained by neutralizing the acid with sodium oxide, hydroxide or carbonate or by oxidizing sodium selenite. Slightly soluble in water, below 32 °C it crystallizes from aqueous solutions in the form of decahydrate Na 2 SeO 4 10H 2 O
Hydrogen selenide, H 2 Se- a colorless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. The most toxic selenium compound. In air it is easily oxidized at ordinary temperatures to free selenium. It is also oxidized to free selenium by chlorine, bromine and iodine. When burned in air or oxygen, selenium(IV) oxide and water are formed. Stronger acid than H2S.
Selenides- compounds of selenium with metals. Crystalline substances, often with a metallic luster. There are monoselenides of the composition M 2 Se, MSe; polyselenides M 2 Se n (except Li), where n = 2-6; hydroselenides MHSe. Air oxygen is oxidized to selenium: 2Na 2 Se n + O 2 + 2H 2 O = 2n Se + 4NaOH
Application:
Selenium is used in rectifying semiconductor diodes, as well as for photovoltaic devices, electrophotographic copying devices, as phosphors in television, optical and signal devices, thermistors, etc. Selenium is widely used for decolorizing green glass and producing ruby glasses; in metallurgy - to give steel a fine-grained structure and improve their mechanical properties; in the chemical industry - as a catalyst.
The stable isotope selenium-74 made it possible to create a plasma laser with colossal amplification in the ultraviolet region (about a billion times).
The radioactive isotope selenium-75 is used as a powerful source of gamma radiation for flaw detection.
Biological role and toxicity:
Selenium is present in the active centers of some proteins in the form of the amino acid selenocysteine. It has antioxidant properties, increases the perception of light by the retina, and affects many enzymatic reactions. The requirement of humans and animals for selenium does not exceed 50-100 mcg/kg of diet.
Polkovnikov A.A.
HF Tyumen State University, 581 group. 2011
Chemist's Handbook website:
Selenic acid is an inorganic substance consisting of a selenate anion and a hydrogen cation. Its chemical formula is H 2 SeO 4. Selenic acid, like any other compound, has unique properties due to which it has found wide application in certain areas. And this should be discussed in more detail.
General characteristics
Selenic acid belongs to the strong class. Under standard conditions, it looks like colorless crystals that dissolve well in water. You should be wary of this substance, as it is poisonous and hygroscopic (absorbs water vapor from the air). This compound is also a powerful oxidizing agent. Other characteristics can be identified in the following list:
- The molar mass is 144.97354 g/mol.
- Density is 2.95 g/cm³.
- The melting point reaches 58°C, and the boiling point - 260°C.
- The dissociation constant is -3.
- Solubility in water is achieved at 30 °C.
Interestingly, selenic acid is one of the few substances that can dissolve gold. This list also includes cyanide, Lugol's solution and aqua regia. But among acids it is the only one like this.

Obtaining the substance
Most often, selenic acid is synthesized according to the formula SeO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SeO 4. It shows the interaction between water and selenium oxide. It is an inorganic substance that is easily soluble in acetic anhydride, sulfuric acid, and sulfur dioxide. By the way, selenium compound can decompose into oxide and water under the influence of phosphorus anhydride (P 2 O 5).
In addition, the acid is also obtained as a result of reactions when the main substance reacts with chlorine or bromine water. Here are the formulas used to obtain selenic acid in these two cases:
- Se + 3Cl 2 + 4H 2 O → H 2 SeO 4 + 6HCl.
- Se + Br 2 + 4H 2 O → H 2 SeO 4 + 6HBr.
But these are not the last methods. There are two more. The production of selenic acid from selenium is possible due to its reaction with hydrogen peroxide. It looks like this: SeO 3 + H 2 O 2 → H 2 SeO 4 .

Application
Now we can talk about him. Why is obtaining selenic acid so important? Because without it the synthesis of its salts is impossible. They are better known as selenates. We will talk about them a little later.
The use of selenic acid as an oxidizing agent is very common, since in this process it exhibits much more properties than sulfuric acid. Even if it is diluted. If sulfuric acid has electrode potentials equal to approximately ~0.169 V, then for selenic acid this figure reaches ~1.147 V. And every person, even those not versed in chemistry, will notice the difference.
Needless to say, selenic acid easily oxidizes hydrochloric acid and also dissolves gold, resulting in the formation of selenate of this metal, which is a red-yellow liquid.
Ammonium selenate
The formula of this salt is (NH 4) 2SeO 4. This substance is represented by colorless crystals. They dissolve well in water, but not in acetone or ethanol. They exhibit the general properties of salts.
They are used as insecticides. This is the name of the substances used to kill insects. Ammonium selenate is actively used in disinfestation. But it must be used with extreme caution, as this substance is particularly toxic. But that's why it's effective.

Barium selenate
Its formula is BaSeO 4. This salt, unlike the previous one, does not dissolve in water. But it reacts with, resulting in the formation of selenium and barium sulfate. This is where he is of particular interest. After all, barium sulfate is an X-ray positive substance that is actively used in radiology.
This compound is not toxic. It increases the contrast of the image obtained during x-rays. Sulfate is not absorbed from the digestive tract and does not enter the bloodstream. It is excreted in the stool, so it is harmless to humans. This substance is used in the form of a suspension orally, together with sodium citrate and sorbitol.
Beryllium selenate
This salt with the formula BeSeO 4 forms crystalline hydrates. The substance itself is formed in a very interesting way. It is the result of amphoteric beryllium hydroxide in selenic acid. Dissociation results in the formation of colorless crystals, which decompose when heated.
Where are the notorious hydroxides used? They are usually used as raw materials to obtain beryllium. Or used as a catalyst for polymerization and Friedel-Crafts reactions.

Gold selenate
This substance has the following formula - Au 2 (SeO 4) 3. It looks like small yellow crystals. Naturally, this “salt” does not dissolve in water. It can only be affected by hot concentrated selenic acid. Selenium oxide is not formed as a result of this reaction, but a reddish-yellow solution appears.
The “golden” salt is also soluble in nitric and sulfuric acids. But hydrogen chloride can destroy it.
Obtaining gold selenate is quite quick and simple. A temperature of 230 °C is sufficient to carry out the reaction.
Copper selenate
The formula of this salt looks like this - CuSeO 4. This substance is white, soluble in water (but not in ethanol) crystals, which also form crystalline hydrates.
This salt is obtained according to the following formula: CuO + H2SeO 4 → 40-50°C CuSeO 4 + H 2 O. This reflects the dissolution of the oxide in selenic acid, as a result of which water is also released. By the way, the resulting crystalline hydrates subsequently lose some of the H 2 O. To do this, it is enough to increase the temperature to 110°C. And if it is above 350°C, then the crystalline hydrate will completely begin to decompose.

Sodium selenate
This is the last salt in the formation of which the acid in question is involved. Its formula is Na 2 SeO 4. This compound is of particular interest because it is the result of the reaction of an alkali metal and a strong acid. Salt, by the way, is soluble in water and also forms a crystalline hydrate.
They get it in different ways. The most common involves dissolving selenium in hydrogen peroxide. According to the formula, it looks like this: Se + 2NaOH + 3H 2 O 2 → Na 2 SeO 4 + 4H 2 O.
They also resort to the oxidation of sodium selenite, performed using hydrogen peroxide, electrolysis or oxygen. But the simplest method involves the interaction of the acid in question with sodium carbonate. It is sometimes replaced with hydroxide.
This is perhaps the most actively used selenate. It is used as a medicine. According to ATC, sodium selenate is a mineral supplement. However, neither in the USA nor in Russia, not a single medicine containing it is registered. But in Latvia and Denmark there are such drugs. The same “Bio-Selenium+Zinc”, for example. An excellent remedy for strengthening the immune system.
But selenate is included in biological supplements sold in Russia. The same “Supradin Kids Junior” contains it in the amount of 12.5 mcg per tablet.
In general, it is through the use of this substance that doctors recommend treating selenium deficiency in the body. But, of course, before use it is necessary to undergo a medical examination and consultation.
As you can see, even though selenic acid is not used in its pure form, the importance of its derivatives in chemistry, medicine and industry is obvious.