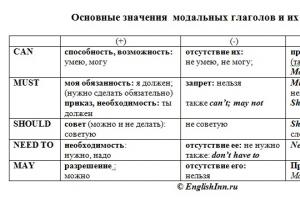
So, dear English Learner, you have studied the theory on the topic and now let's start practicing. Having completed 11 exercises below, you will learn to distinguish the meanings of basic modal verbs can, may, must, should, and make negative and interrogative sentences with them. Below is a brief summary of the main meanings of these verbs.

English modal verbs. Exercises for Beginners (Level 1)
Exercise 1. Choose a modal verb based on its meaning and context. Translate the sentences.
When both verbs seem to fit, choose the more typical situation.
- You (must, can) go to bed now.
- She (may, should) read this book.
- I (must, may) go home.
- He (can, may) speak English.
- The students (must, may) use a calculator at the Maths lessons.
- My mother (can, should) cook many delicious dishes.
- My father (must, can) drive a car.
- Jack (can, must) play the guitar very well.
- You (should, must) ask his advice.
- Kate (may, can) remember a lot of words.
Exercise 2. Make these sentences that contain modal verbs negative.
- You must read in bed.
- You can cross the road when the lights are red.
- You should open the window. It is cold outside.
- It is already late. She must go outside.
- He should dress so formal if he goes to a picnic.
- You must keep books at home for so long.
- You can park here.
- Students may shout at the lessons.
- Teachers may be late for school.
- Parents must obey their children. ( obey- obey)
Exercise 3. Make these sentences interrogative.
- She can play chess.
- He can play hockey.
- They may go to the cinema.
- I may open the window.
- Children and adults must clean their teeth twice a day. (How often...?)
- Children must go to school. (Where...?)
- English learners must learn English words every day. (What...?)
- You should keep your room tidy. (What...?) ( keep tidy- keep in order)
- Children should listen to their parents' advice.
- They should be polite.
Exercise 4. Make up questions from words and give short or full answers to them.
- your brother/ play/ table tennis/ can? - Yes, he...
- your cousin/ can/ ride a horse? - No, he...
- may/ go to/ I / the cinema? - Yes, you...
- late/ may/ come home/ she? - No, she...
- learn this poem/ must/ she/ by heart? - Yes, she...
- books/ how many/ they/ must/ read? – Only two.
- wear/ smart clothes/ for the party/ should/ they? - Yes,...
- salt/ how much/ should/ put in the dish/ I ? - Just a little.
- the student/ mobile/ phones/ use/ can/ at the exams? - No, they...
- children/ come to school / in time/ must? - Yes, they...
Exercise 5. Find errors.
- You don't can go to the party.
- He must take his dog for a walk.
- I can help you.
- He should not be late.
- Can his brother speak French?
- Paul must go there.
- You don't must smoke here.
Exercise 6. Select the correct CAN'T or COULDN'T option.
Beginners need to remember that the modal verb CAN has a past tense form - COULD.
- When my sister was a little girl, she (can’t / couldn’t) read.
- You (can/ could) see this picture in the Tretyakov Gallery.
- Yesterday I lost my keys and (can’t / couldn’t) get into my flat.
- I (can’t/ couldn’t) go out because I have a lot of work.
- He (can’t /couldn’t) speak English when he was 10.
Remember that CAN'T and MUSTN'T are often translated as IMPOSSIBLE.
Remember that
CAN’T - IMPOSSIBLE (general rule, prohibition)
MUSTN’T - IMPOSSIBLE (personal decision of the speaker)
Exercise 7. Tell me what NOT to do. Use verbsCAN'T andMUSTN'T.
- You _____ tell anybody about it. It is a secret.
- The baby _______ drink cold milk.
- You ______ cross the street here.
- You _______speak so loudly. It is very late.
- Little children _____ leave home alone.
Exercise 8. Translate the sentences with the expression IMPOSSIBLE. Use the verbs CAN’T (general rule, prohibition) and MUSTN’T (speaker’s decision).
- He should not drink cold milk. He's sick. (be ill.)
- She can't eat oranges.
- We can't run around here.
- You cannot talk loudly in the library. (at the library.)
- You can't smoke here.
Exercise 9. Provide advice to teachers and students using should (shouldn't), based on the context.
Remember! Should is advice that is not mandatory.
Teachers/Students
explain the rules very well, get bad marks, give instructions, give bad marks, give nicknames, answer questions
Exercise 10. Translate sentences with forms of modal verbs into English.
- He must... _____________ learn new English words.
- She can... ______________play the guitar.
- People should... ____________ be careful when crossing the street.
- Drivers should not... __________drive fast.
- She is allowed... ____________go to the cinema today?
- I can’t... ____________ come home late.
- I can’t... _____________ speak English well.
- Children are not allowed to... ____________run here.
- They are not allowed...___________play computer games.
- You should...___________ try again.
Exercise 11. Translate sentences with modal verbs.
- I don't know how to play the guitar.
- He doesn't know how to play table tennis.
- Do you know how to ride a bike?
- Does your sister know how to drive?
- Can you give me your pen?
- Very hot. Can you open the window?
- Can I go to the cinema?
- Can I use a calculator?
- You must learn English words every day.
- You should read books in English.
- Adults should not yell at children.
- You must not (cannot) use a mobile phone during the exam.
- study
- continue
1. Translate the sentences and determine the meaning of the modal verb (ability or inability to do something, expression of doubt, bewilderment, prohibition or permission, polite request).
- You can't be rude to your sister.
- Could you drive me to work?
- Could Greg have said this?
- Next year I’ll be able to speak English fluently.
- I’m sorry but I can’t come to the party.
- You can take my dictionary if you need it.
- My old grandparents are not able to look after themselves.
- Can she still be having a shower?
- Could you close the door?
- I will be able to play billiards with you tonight.
2. Convert the sentences to Past Simple. Make the necessary changes.
Reference: Sally can speak on the phone for hours. – Sally could speak on the phone for hours.
- I can dance a waltz round the room right now. (last night)
- My little son can read 100 words a minute. (when he was six)
- No, he can’t be in London now. (yesterday)
- Cindy can't carry this heavy box.
3. Convert the sentences to the past tense, Future Simple. Make the necessary changes.
No.: I can join you today. (next Sunday) – I will be able to join you next Sunday.
- He can't lend you his bike. (tomorrow)
- We can buy some aspirin at the chemist’s.
- Dad can sell his car now. (when he reduces the price)
- Our managers can solve the problem. (next week)
4. Fill in the blanks with modal verbs can, could, be able to in the required form.
- Rita … cook perfect steaks as the meat was fresh.
- You … work as a waiter until you are 18.
- I don't believe the latest news. It... be true!
- When he lived in Canada he … speak French quite well.
- We … see the ballet better if we buy the first row tickets.
- Mary is depressed, she... stop crying.
- Mother caught a taxi because she had a terrible backache, and she… walk.
- …do you speak slower, please?
- I ... play the violin now but I ... play it two years ago.
- You... get to the station in half an hour.
Answers:
- Ban (You cannot be rude to your sister.)
- Request (Could you give me a ride to work?)
- Doubt, bewilderment (Could Greg really say that?)
- Ability (Next year I will be able to speak English fluently.)
- Inability (Sorry, but I can't come to the party.)
- Permission (You can borrow my dictionary if you need to.)
- Inability (My old grandparents can't take care of themselves.)
- Confusion (How can she still shower?)
- Request (Could you close the door?)
- Ability (I can play billiards with you tonight.)
- I could dance a waltz round the room last night. (I was able to waltz across the room last night.)
- My little son could read 100 words a minute when he was six. (My little son could read 100 words per minute at age 6.)
- No, he couldn’t be in London yesterday. (No, he couldn't have been in London yesterday.)
- Cindy couldn't carry this heavy box. (Cindy couldn't carry that heavy box.)
- He won’t be able to lend you his bike tomorrow. (He won't be able to lend you his bike tomorrow.)
- We’ll be able to buy some aspirin at the chemist’s. (We can buy aspirin at the pharmacy.)
- Dad will be able to sell his car when he reduces the price. (Dad can sell his car when he lowers the price.)
- Our managers will be able to solve the problem next week. (Our managers will be able to resolve this issue next week.)
- Could (Rita was able to cook excellent steaks because the meat was fresh.)
- won’t be able to (You will not be able to work as a waiter until you are 18 years old.)
- can’t (I don’t believe the latest news. It can’t be true!)
- Could (When he lived in Canada, he could speak French quite well.)
- will be able to (We can see the ballet better if we buy tickets in the first row.)
- can’t (Mary is depressed, she cries non-stop.)
- couldn’t (Mom caught a taxi because she had severe back pain and could not walk.)
- Could (Could you speak more slowly?)
- can – couldn’t (I can play the violin now, but I couldn’t play it two years ago.)
- will be able to (You will be able to get to the station in half an hour.)
As in Russian, in English there are words that denote actions - verbs. As a rule, verbs have a special form - the infinitive , consisting of the base form of the verb preceded by a particle to. Typically, this form is used to represent English verbs. For example, in a word list, verbs might be represented as follows:
to swim - to swim
to read - read
to dance - to dance
It is worth noting that in this case the particle to is not translated, and only means that the verb is given in its basic form.
Modal verb can
Meaning and usage
In English, some verbs are combined into a special group and called modal verbs. Modal verbs do not denote any action, they only denote an attitude towards the action. For example, a representative of this group is the verb can, which translates as be able to or be able. It does not denote the action itself, but only the ability or ability to perform it.
Verb can used with the infinitive of another verb without a particle to.
To form a negative form of a verb can need to attach a particle not:
In colloquial speech, abbreviated negative forms are often used:
In interrogative sentences the verb can placed in front of the underlying:
Short answers to questions with verb can will look like this:
| Question | YES | NO |
|---|---|---|
| Can you...? | Yes, I/we can . | No, I/we can't . |
| Can he/she/it/they ...? | Yes, he/she/it/they can. | No, he/she/it/they can't. |
| Can I/we...? | Yes, you can. | No, you can't. |
At the elementary level, every student learns the modal verb 'can'. Typically, to practice grammar, students complete tasks such as filling in the blanks, making sentences based on pictures, and talking about what they can and cannot do. How to diversify these exercises? We offer fun exercises for practicing the modal verb ‘can’ (to reflect physical or mental ability, ability to do something).
Exercise 1 -- Creating memes or drawing pictures
What picture do you think students will remember better for the phrase “It can fly”?

Most likely the second one, since this picture is funny, memorable and unusual. To introduce and practice grammar, choose funny pictures,or just photographs instead of pictures from textbooks, which do not evoke any emotional responses in students.
If you are limited in time and cannot find suitable pictures, ask students to get creative and complete the drawings to make a suitable sentence.I really like to use pictures with cats (especially for lessons with children, such pictures really amuse children). Show students the sample sentence “It can swim.”

Give out sentences with the verb ‘can’ and ask them to complete the picture so that it matches the sentence.
Exercise 2 -- Unusual Features
We will work on developing students' creative and critical thinking. Offer two nouns, students must complete the sentence “they both can...”
For example, a parrot and a child -- they both can speak. Make the list more complex (add something that is completely different from each other - a tortoise and a tree - they both can live long), organize a competition for the most unusual possibilities that students can come up with for these pairs.
Instead of pairs of words, you can use pictures, so students will remember not only verbs, but also nouns. To make it more interesting for children and teenagers to complete the task, choose funny pictures. My children like the animals drawn in one “round” style
. The group that makes the most “they both can...” sentences receives a sticker with an animal from this collection.
It will be interesting for younger schoolchildren to talk about superheroes. Show gifs of their favorite characters and discuss what they can and can't do.
Exercise 3 -- Writing sentences
To add a gamification element to writing positive and negative sentences, use a coin. Flip a coin; if it comes up heads, make positive suggestions; if it comes up tails, make negative suggestions. There are many online coins, for example pumpkin video and, of course, songs from SuperSimpleSongs.
Game techniques for practicing the use of the verb can. 2nd grade.
These game techniques contribute to the high activity of students; the readiness and desire to take part in the game helps to form solid knowledge on the topic being studied.
"True or false"
The goal is to practice using the verb can in affirmative and negative sentences.
Equipment – pictures on the topic “sports”.
Game scenario:
The teacher shows students pictures of people involved in various sports. Showing a picture, the teacher says what the person depicted on it can do. If the teacher is right, the children say: “Yes, he/she can.” If the teacher is wrong, the children say: “No, he/she can`t.”
"Be surprised"
The goal is to practice using the verb can in interrogative and affirmative sentences.
Game scenario:
The student (driver) comes up with a proposal about what he can do. For example: I can swim. The task of the others is to express surprise: Can you? (can be carried out in a chain, in mode P.1, P.2, P.3...).
"Guess"
The goal is to practice using the verb can and vocabulary on the topic “sport.”
Game scenario:
The driver turns his back to the class. The actor is depicting some kind of sports game. The presenter guesses what kind of game it is (what kind of sport he knows how to play) by asking questions: “Can he/she ...?” The class answers the leader’s questions in unison: “Yes, he/she can” or “No, he/she can`t.”
“Can/can’t”
The goal is to train the use of the verb can.
Equipment – pictures of people performing various actions.
Game scenario:
A table consisting of two columns is drawn on the board:
He/she can…
He/she can`t…
Next to it is a list of action verbs. For example: jump, fly, swim...
The teacher shows pictures of people performing some action, the children make sentences based on them, go to the board and write them down in the appropriate column of the table.
"Cubes"
The goal is to practice the verb can and vocabulary on the topic “sport”.
Equipment is a cube, on the sides of which various objects for playing sports are depicted (skis, ball, skates...).
Game scenario:
Children toss the cube and, looking at the picture, say whether they can do it or not, then ask the question to the next student, passing the cube to him.
P.1 – Skate. I can skate. P.2, can you skate?
P.2 – I can`t skate. (rolls the dice).Swim. I can swim. P.3 ,can you swim?...
6. "Lazy-bones"
The goal is to initially consolidate the use of negative sentences with the verb can.
Game scenario:
The teacher asks students to perform some action, and they say that they do not know how to do it. For example:
T.- Please, dance.
P.- I can`t dance.
7. "Nonsense"
The goal is to train the use of the verb can in negative sentences.
Equipment - stars.
Game scenario:
The teacher names sentences that are not true, for example: “Cats can fly.” Students correct phrases that are incorrect from their point of view. For correct correction, the student receives a star. The one with the most stars on his desk at the end of the game wins.
"Climb the tower"
The goal is to train the ability to translate different types of sentences with the verb can from Russian into English.
Equipment – a drawing depicting a tower; numbers 1, 2, 3; offers.
Game scenario:
The class is divided into three groups. A drawing depicting a tower with steps is hung on the board. The number of steps depends on the number of proposals. Cards with numbers corresponding to each team are placed on the first step of the tower. Suggestion cards are placed on the teacher's desk, written down. A representative from each team takes a proposal card and discusses the translation of the proposal with the team. If the transfer is successful, the team moves up one step. If the answer is incorrect, the team remains on the same step. The team that reaches the top of the tower first wins.
Suggestions for translation:
I can sing.
Crocodiles can swim.
Cats can't fly.
Can bears jump?
Can elephants dance?