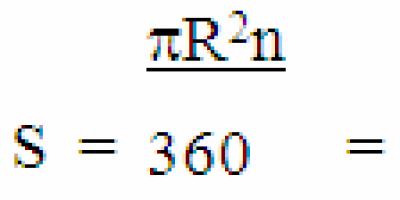Area formula is necessary to determine the area of a figure, which is a real-valued function defined on a certain class of figures of the Euclidean plane and satisfying 4 conditions:
- Positivity - Area cannot be less than zero;
- Normalization - a square with side unit has area 1;
- Congruence - congruent figures have equal area;
- Additivity - the area of the union of 2 figures without common internal points is equal to the sum of the areas of these figures.
| Geometric figure | Formula | Drawing |
|---|---|---|
|
The result of adding the distances between the midpoints of opposite sides of a convex quadrilateral will be equal to its semi-perimeter. |
||
|
Circle sector. The area of a sector of a circle is equal to the product of its arc and half its radius. |
|
|
|
Circle segment. To obtain the area of segment ASB, it is enough to subtract the area of triangle AOB from the area of sector AOB. |
S = 1 / 2 R(s - AC) |
|
|
The area of the ellipse is equal to the product of the lengths of the major and minor semi-axes of the ellipse and the number pi. |
|
|
|
Ellipse. Another option for calculating the area of an ellipse is through two of its radii. |
|
|
|
Triangle. Through the base and height. Formula for the area of a circle using its radius and diameter. |
||
|
Square . Through his side. The area of a square is equal to the square of the length of its side. |
|
|
|
Square. Through its diagonals. The area of a square is equal to half the square of the length of its diagonal. |
||
|
Regular polygon. To determine the area of a regular polygon, it is necessary to divide it into equal triangles that would have a common vertex at the center of the inscribed circle. |
S= r p = 1/2 r n a |
A triangle is a flat geometric figure with one angle equal to 90°. Moreover, in geometry it is often necessary to calculate the area of such a figure. We will tell you how to do this further.
The simplest formula for determining the area of a right triangle
Initial data, where: a and b are the sides of the triangle extending from the right angle.
That is, the area is equal to half the product of the two sides that come out of the right angle. Of course, there is Heron's formula used to calculate the area of a regular triangle, but to determine the value you need to know the length of the three sides. Accordingly, you will have to calculate the hypotenuse, and this is extra time.
Find the area of a right triangle using Heron's formula
This is a well-known and original formula, but for this you will have to calculate the hypotenuse on two legs using the Pythagorean Theorem.
In this formula: a, b, c are the sides of the triangle, and p is the semi-perimeter.
Find the area of a right triangle using the hypotenuse and angle
If none of the legs are known in your problem, then you will not be able to use the simplest method. To determine the value you need to calculate the length of the legs. This can be done simply by using the hypotenuse and the cosine of the adjacent angle.
b=c×cos(α)
Once you know the length of one of the legs, using the Pythagorean theorem you can calculate the second side coming out of the right angle.
b 2 =c 2 -a 2
In this formula, c and a are the hypotenuse and leg, respectively. Now you can calculate the area using the first formula. In the same way, you can calculate one of the legs, given the second and the angle. In this case, one of the required sides will be equal to the product of the leg and the tangent of the angle. There are other ways to calculate area, but knowing the basic theorems and rules, you can easily find the desired value.
If you do not have any of the sides of the triangle, but only the median and one of the angles, then you can calculate the length of the sides. To do this, use the properties of the median to divide a right triangle into two. Accordingly, it can act as a hypotenuse if it comes out of an acute angle. Use the Pythagorean theorem and determine the length of the sides of the triangle coming from the right angle.


As you can see, knowing the basic formulas and the Pythagorean Theorem, you can calculate the area of a right triangle, having only one of the angles and the length of one of the sides.
The area of a right triangle can be found in several ways. A right angle in any figure adds properties to it and this can be used to correctly and quickly solve problems.
Right triangle
First, let's discuss the right triangle itself, its features and properties. A right triangle is a triangle that contains an angle.
A right triangle cannot be obtuse, because then the sum of the angles of the triangle will exceed 180 degrees, and this is impossible.
In a right triangle, two of the three altitudes coincide with the sides - the legs. For the same reason, the point of intersection of the altitudes of a right triangle coincides with the vertex at a right angle.

Rice. 1. All heights of a right triangle.
The same point will be the center of the circumscribed circle.
Area of a triangle
The area of a triangle is usually found using the standard formula, as half the product of the base and the height drawn to this base.
$$S=(1\over2)*a*h$$
You can find the area as half the product of the sides and the sine of the angle between them:
$$S=(1\over2)*a*b*sin(g)$$
There are complicated formulas for finding area, but they are used extremely rarely.
Area of a right triangle
The area of a right triangle is found using the same formulas, but in some cases these formulas can be simplified.
For example, you can take advantage of the fact that the altitudes in a right triangle coincide with the legs. Then the standard formula becomes:
$S=(1\over2)*a*b$, where a and b are the legs of a right triangle.
This is one of the simplest formulas for the area of a right triangle. Let's try to transform the second formula.
$$S=(1\over2)*a*b*sin(g)$$
If we remember that the sine of an angle is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. In our case, we denote the opposite leg as the letter f, because a is an adjacent leg, and an acute angle can only be concluded between the leg and the hypotenuse. So b is the hypotenuse.
$S=(1\over2)*a*b*sin(g)= (1\over2)*a*b*(f\over(b))=(1\over2)a*f$ - everything turns out the same same formula.

Rice. 2. Drawing to conclusion.
This means that we carried out the first conclusion correctly, and a right triangle has only one special formula for finding the area. If it does not work, you can use general formulas. These are two possible ways to calculate the area.
For example, if the hypotenuse is known according to the conditions of the problem, then you can try to find the height falling on the hypotenuse and determine the area using the general formula. Using the same principle, you can find the area through the sine if the hypotenuse and leg are known.

Rice. 3. Height drawn to the hypotenuse.
The main thing to remember is that any problem always has 3 solutions and solve each in the most convenient way.
What have we learned?
We talked about right triangles and derived the formula for the area of a right triangle using the legs. We discussed the general formulas for the area of triangles and said that each of these formulas would work for solving a right triangle.
Test on the topic
Article rating
Average rating: 4.5. Total ratings received: 115.
A right triangle is found in reality on almost every corner. Knowledge of the properties of a given figure, as well as the ability to calculate its area, will undoubtedly be useful to you not only for solving geometry problems, but also in life situations.
Triangle geometry
In elementary geometry, a right triangle is a figure that consists of three connected segments that form three angles (two acute and one straight). The right triangle is an original figure characterized by a number of important properties that form the foundation of trigonometry. Unlike a regular triangle, the sides of a rectangular figure have their own names:
- The hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle, opposite the right angle.
- Legs are segments that form a right angle. Depending on the angle under consideration, the leg can be adjacent to it (forming this angle with the hypotenuse) or opposite (lying opposite the angle). There are no legs for non-right triangles.
It is the ratio of the legs and hypotenuse that forms the basis of trigonometry: sines, tangents and secants are defined as the ratio of the sides of a right triangle.
Right triangle in reality
This figure has become widespread in reality. Triangles are used in design and technology, so calculating the area of a figure has to be done by engineers, architects and designers. The bases of tetrahedrons or prisms - three-dimensional figures that are easy to meet in everyday life - have the shape of a triangle. Additionally, a square is the simplest representation of a "flat" right triangle in reality. A square is a metalworking, drawing, construction and carpentry tool that is used to construct angles by both schoolchildren and engineers.
Area of a triangle
The area of a geometric figure is a quantitative estimate of how much of the plane is bounded by the sides of the triangle. The area of an ordinary triangle can be found in five ways, using Heron's formula or using such variables as the base, side, angle and radius of the inscribed or circumscribed circle. The simplest formula for area is expressed as:
where a is the side of the triangle, h is its height.
The formula for calculating the area of a right triangle is even simpler:
where a and b are legs.
Working with our online calculator, you can calculate the area of a triangle using three pairs of parameters:
- two legs;
- leg and adjacent angle;
- leg and opposite angle.
In problems or everyday situations you will be given different combinations of variables, so this form of the calculator allows you to calculate the area of a triangle in several ways. Let's look at a couple of examples.
Real life examples
Ceramic tile
Let's say you want to cover the kitchen walls with ceramic tiles, which have the shape of a right triangle. In order to determine the consumption of tiles, you must find out the area of one cladding element and the total area of the surface being treated. Let's say you need to process 7 square meters. The length of the legs of one element is 19 cm, then the area of the tile will be equal to:
This means that the area of one element is 24.5 square centimeters or 0.01805 square meters. Knowing these parameters, you can calculate that to finish 7 square meters of wall you will need 7/0.01805 = 387 elements of facing tiles.
School task
Let's say in a school geometry problem you need to find the area of a right triangle, knowing only that the side of one leg is 5 cm, and the opposite angle is 30 degrees. Our online calculator comes with an illustration showing the sides and angles of a right triangle. If side a = 5 cm, then its opposite angle is angle alpha, equal to 30 degrees. Enter this data into the calculator form and get the result:
Thus, the calculator not only calculates the area of a given triangle, but also determines the length of the adjacent leg and hypotenuse, as well as the value of the second angle.
Conclusion
Right triangles are found in our lives literally on every corner. Determining the area of such figures will be useful to you not only when solving school assignments in geometry, but also in everyday and professional activities.
In geometry class in high school, we were all told about triangles. However, as part of the school curriculum, we receive only the most necessary knowledge and learn the most common and standard methods of calculation. Are there any unusual ways to find this quantity?
As an introduction, let us remember which triangle is considered right-angled, and also denote the concept of area.
A right triangle is a closed geometric figure, one of the angles of which is equal to 90 0. Integral concepts in the definition are legs and hypotenuse. Legs mean two sides that form a right angle at the point of connection. The hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle. A right triangle can be isosceles (its two sides will be the same size), but it will never be equilateral (all sides will be the same length). We will not discuss the definitions of height, median, vectors and other mathematical terms in detail. They are easy to find in reference books.
Area of a right triangle. Unlike rectangles, the rule about

the work of the parties in the determination does not apply. If we speak in dry terms, then the area of a triangle is understood as the property of this figure to occupy a part of the plane, expressed by a number. Quite difficult to understand, you will agree. Let's not try to delve deeply into the definition; that's not our goal. Let's move on to the main thing - how to find the area of a right triangle? We will not perform the calculations themselves, we will only indicate the formulas. To do this, let's define the notation: A, B, C - sides of the triangle, legs - AB, BC. Angle ACB is straight. S is the area of the triangle, h n n is the height of the triangle, where nn is the side on which it is lowered.
Method 1. How to find the area of a right triangle if the size of its legs is known
Method 2. Find the area of an isosceles right triangle
Method 3. Calculating area using a rectangle
We complete the right triangle to a square (if the triangle

isosceles) or rectangle. We get a simple quadrilateral made up of 2 identical right triangles. In this case, the area of one of them will be equal to half the area of the resulting figure. S of a rectangle is calculated by the product of the sides. Let's denote this value M. The desired area value will be equal to half M.
Method 4. “Pythagorean pants.” The famous Pythagorean theorem
We all remember its formulation: “the sum of the squares of the legs...”. But not everyone can

say, what does some “pants” have to do with it? The fact is that Pythagoras initially studied the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Having identified patterns in the ratio of the sides of squares, he was able to derive a formula known to all of us. It can be used in cases where the size of one of the sides is unknown.
Method 5. How to find the area of a right triangle using Heron's formula
This is also a fairly simple method of calculation. The formula involves expressing the area of a triangle through the numerical values of its sides. For calculations, you need to know the sizes of all sides of the triangle.
S = (p-AC)*(p-BC), where p = (AB+BC+AC)*0.5
In addition to the above, there are many other ways to find the size of such a mysterious figure as a triangle. Among them: calculation by the inscribed or circumscribed circle method, calculation using the coordinates of vertices, the use of vectors, absolute value, sines, tangents.