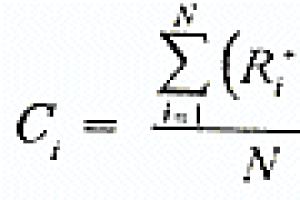The Russian language has 21 consonants and 37 consonant sounds:
| Letter | Sounds | Letter | Sounds | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | [b], [b"] | P | [P], [P"] | |
| IN | [V], [V"] | R | [R], [R"] | |
| G | [G], [G"] | WITH | [With], [With"] | |
| D | [d], [d"] | T | [T], [T"] | |
| AND | [and], [and"] | F | [f], [f"] | |
| Z | [h], [z"] | X | [X], [X"] | |
| Y | [th"] | C | [ts] | |
| TO | [To], [To"] | H | [h"] | |
| L | [l], [l"] | Sh | [w] | |
| M | [m], [m"] | SCH | [sch"] | |
| N | [n], [n"] |
Consonant sounds are hard and soft, voiced and voiceless. The softness of sound in transcription is indicated by [ " ].
Hard and soft consonants
A hard consonant sound is produced if there is a vowel after the consonant. A, O, U, S or E:
na lo ku we fe
A soft consonant sound is produced if there is a vowel after the consonant E, Yo, I, Yu or I:
be le ki nu la
The softness of consonant sounds is also indicated using a soft sign - b. The soft sign itself does not indicate sound. It is written after a consonant and together with it denotes one soft consonant sound:
lynx [trot"], fire [fire"], snowstorm [in "th" uga].
Most consonant letters correspond to two sounds: hard and soft; such consonants are called paired.
Paired consonants for hardness - softness:
But there are consonant letters that correspond to only one of the sounds: hard or soft. Such consonants are called unpaired.
Unpaired hard consonants(always hard):
AND [and], Sh [w], C [ts].
Unpaired soft consonants(always soft):
H [h"], SCH[sch"], Y [th"].
In Russian there is a long voiced soft sound [ and"]. It occurs in a small number of words and is obtained only when pronouncing combinations of letters LJ, zzh, zhd:
reins, rattle, rain.
Voiced and voiceless consonants
Consonant sounds can be divided into voiceless and voiced.
Voiceless consonants are those sounds that are not produced using the voice. They consist only of noise. For example: sounds [ With], [w], [h"].
Voiced consonants are those sounds that use the voice in their pronunciation, that is, they consist of voice and noise. For example: sounds [ R], [and], [d].
Some sounds form a pair: voiced - voiceless, such sounds are called paired.
Paired consonants according to deafness - voicing:
Unpaired voiced consonants: J, L, M, N, R.
Unpaired voiceless consonants: X, C, Ch, Shch.
Hissing and whistling consonants
Sounds [ and], [w], [h"], [sch"] are called hissing consonants. Sounds [ and] And [ w] are unpaired hard hissing consonant sounds:
bug [bug], jester [jester]
Sounds [ h"] And [ sch"] are unpaired soft hissing consonant sounds:
siskin [h"izh], shield [shield]
Sounds [ h], [z"], [With], [With"], [ts] are called whistling consonants.
Letter and sound Y
Letter Y(and short) denotes the sound [ th"]: paradise [paradise"].
Letter Y is written:
- At the beginning of the words:
iodine, yogurt.
- In the middle of words, before consonants:
husky, T-shirt, coffee pot.
- At the end of the words:
paradise, may, yours.
Sound [ th"] letters are more common Y, since it appears in words where there is no letter Y, but there are vowels I, E, Yu And Yo. Let's consider in what cases the sound [ th"] occurs in words that do not contain a letter Y:
- vowels I, E, Yu And Yo come at the beginning of the words:
pit [th "ama],
- vowels I, E, Yu And Yo come after vowels:
blowing [blow it],
- vowels I, E, Yu And Yo stand after the dividing symbol ( Kommersant):
entry [vy"ezd],
- vowels I, E, Yu And Yo stand after the soft separating sign ( b):
it's pouring [l"th"from],
- vowel AND comes after the separating soft sign ( b):
hives [st "y"].
Cards - hard and soft consonants
In continuation of the post “How to teach a child to read by syllables? Making words from syllables,” I offer you new material - cards with hard and soft consonant sounds.
Use the cards to teach your child to determine when consonants are soft and when they are hard.
Blue - solid
Green - soft

Consonant sounds can be soft or hard. For example, in the word “world” you hear a soft consonant zyuk [m”], and in the word “poppy” you hear a hard consonant sound [m]. The softness of a consonant is indicated by adding the symbol “to its notation, for example: [m"].
Remember:
Always soft sounds: [th’], [h’], [sh’].
Always hard sounds: [zh], [sh], [ts].
The remaining sounds are soft if they are immediately followed by the vowels e, ё, i, yu, я or ь, and hard if they are followed by other vowels and consonants.


Hard and soft consonants differ in the position of the tongue.
When pronouncing soft consonants ([b"], [v"], [d"], [z"], etc.), the entire body of the tongue moves forward, and the middle part of the back of the tongue rises to the hard palate. This movement of the tongue is called palatalization. Palatalization is considered an additional articulation: it is superimposed on the main one associated with the formation of an obstruction.
When pronouncing hard consonants ([b], [v], [d], [z], etc.), the tongue does not move forward and its middle part does not rise.
Consonants form 15 pairs of sounds contrasting in hardness/softness. All of them are either hard doubles or soft doubles:
[b] - [b"]
[in] - [in"]
[g] - [g"]
[d] - [d"]
[z] - [z"]
[p] - [p"]
[f] - [f"]
[k] - [k"]
[t] - [t"]
[s] - [s"]
[mm"]
[n] - [n"]
[r] - [r"]
[l] - [l"]
[x] - [x"]








Usually, children do not have serious difficulties understanding the difference between vowels and consonants. But we should dwell in more detail on hard and soft consonants.
How to teach children to distinguish between hard and soft consonants
The very first thing you need to teach your child: consonant sounds can be hard and soft, but not letters.
Typical error:
Children confuse sounds and letters. We remember that a sound sounds, and a letter is an icon, it is written. A letter cannot be hard or soft; only a consonant sound can be hard or soft in pronunciation.
Sometimes children can easily learn to distinguish soft and hard sounds by ear.
But it happens that this is difficult, and in this case signs will come to the rescue by which you can distinguish hard sounds from soft ones.
Distinctive features of soft and hard sounds
What sound comes after a consonant:
- If after a consonant there is a vowel a, o, u, e, s, then the consonant is hard.
- If after a consonant there is a vowel and, e, yu, i, then the consonant is soft.
Working on examples:
In the words “mama” and “nora” the consonants are hard, because they are followed by “a” and “o”.
In the words “fly” and “nanny” the consonants are soft because they are followed by “e”, “i”, “ya”.
- If another consonant sounds after a consonant, then the first consonant will be hard.
- There are sounds that can only be hard and sounds that can only be soft, no matter what sound is heard or what letter is written after them.
Always hard sounds - zh, sh, ts.
Always soft - th, h, shch.
A common way to learn these sounds is a simple technique: we write the letters that convey these sounds on a line, and emphasize “th, ch, sch.” The underscore symbolizes the cushion on which the soft sounds sit. The pad is soft, which means the sounds are soft.
Soft sign and hard sign
- If there is a consonant at the end of a word and the letter “b” after it, then the consonant is soft.
This rule is easy to apply if the child sees the written word, but it will not help if the child performs the task by ear.
Movement of the tongue when pronouncing soft and hard sounds
When pronouncing a soft sound, the tongue moves slightly forward, approaching (or touching) the palate with its middle.
When pronouncing hard sounds, the tongue does not move forward.
Table of signs of hard and soft sounds
Solid:
- Before a, o, y, e, y.
- At the end of a word before a consonant.
- F, c, w.
Soft:
- Before the vowels e, e, i, yu, i.
- If after a consonant there is a soft sign (dust, measles).
- Y, h, sch.
A picture or simply a list of thematic words is shown, and the task is given to choose words with soft or hard consonants. For example:


Voiced and voiceless consonants
There are 11 pairs of voiced/voiceless consonants in the Russian language.
The phonetic difference between voiced and voiceless consonants lies in the tension of the vocal cords. Voiceless sounds are pronounced with the help of noise, without straining the ligaments. Voiced sounds are pronounced by voice and are caused by vibration of the vocal cords, because air comes out of the larynx noisily.

Mnemonic technique for memorizing voiceless sounds:
Learn the phrase: “Styopka, do you want some cheek? - Fi! All consonant sounds here are unvoiced.
Examples of tasks for children
Tasks for training the differences between paired consonants can be compiled for each pair according to the following principle (using the example of the D/T pair):

Tasks for distinguishing a pair of consonants G/K

Consonant sounds sound different in different words. Somewhere it’s hard, and somewhere it’s soft. In this lesson we will learn to distinguish between soft and hard consonant sounds and to indicate the softness of consonant sounds in writing with the letters I, E, E, Yu, I and b. Let's find out which consonants form hard-soft pairs, and which are only hard or only soft.
If you ask what can be soft, probably everyone will immediately say: bread, sofa, scarf, pillow. But stone, ice, wood are hard. Yes, but it turns out that the sounds of Russian speech, consonants, can be hard and soft.
Say the words several times in turn: CAT - WHALE.
Compare the first consonants. When pronouncing the sound in the word KIT, the middle part of the tongue rises to the palate, the passage through which air flows narrows, and a sound is obtained, which scientists conventionally call soft. And the opposite sound was called - solid.
It is important to listen to the sounds of spoken words. If you say the word NOS otherwise - with a hard first sound, we get a completely different word - NOSE.
Let's listen and watch the movement of our tongue:
row - sound [p’] - rad - sound [p]
hatch - sound [l’] - bow - sound [l]
crumpled - sound [m’] - small - sound [m]
Sounds can be written (conventionally) using icons. Musical sounds are written in notes, and speech sounds are written in letters, but in special square brackets - in transcription. In order not to confuse hard and soft sounds when reading the transcription, scientists agreed to show the softness of the sound with an icon very similar to a comma, only they put it on top.
Most consonant sounds form pairs based on softness and hardness:
[b] | [b’] |
[V] | [V'] |
[G] | [G'] |
[d] | [d’] |
[z] | [z’] |
[To] | [To'] |
[l] | [l’] |
[m] | [m’] |
[n] | [n’] |
[P] | [P'] |
[R] | [R'] |
[With] | [With'] |
[T] | [T'] |
[f] | [f’] |
[X] | [X'] |
Some consonants are only hard or only soft. They do not form pairs in terms of hardness/softness:
— Only hard consonants: [zh], [w], [ts];
— Only soft consonants: [th’], [h’], [sch’].
In writing, the hardness of consonant sounds is indicated by the vowels A, O, U, Y, E, and the softness of consonant sounds is indicated by the vowels E, Yo, I, Yu, Ya.
There are words with soft consonant sounds at the end of words or in the middle of words before other consonant sounds. Listen to the words: salt, horse, notebook, coat, ring, letter. Then a soft sign will come to the rescue. Even his name suggests - a sign soft, for soft consonants.
How to act when writing words:
- I hear a hard consonant sound - after it I write the letters in place of the vowel sound: A, O, U, Y, E.
- I hear a soft consonant sound before a vowel sound - I denote its softness with vowels: E, Yo, I, Yu, Ya.
- I hear a soft sound at the end of a word or before a consonant sound - I show softness b.
If you liked it, share it with your friends:
Join us onFacebook!
See also:
Preparation for Russian language exams:
The most necessary from the theory:
We suggest taking tests online: