Basic concepts on the topic:
1. Trial, elementary outcome, trial outcome, event.
2. Certain event, impossible event, random event.
3. Joint events, incompatible events, equivalent events, equally possible events, the only possible events.
4. Complete group of events, opposite events.
5. Elementary event, composite event.
6. The sum of several events, the product of several events. Their geometric interpretation
1. In the problem “Two shots are fired at the target. Find the probability that the target will be hit once" by the test is:
1) * two shots are fired at the target;
2) the target will be hit once;
3) the target will be hit twice.
2. Throw a coin. Event: A - “the coat of arms will fall out”. The event - “a number will come up” is:
1) random;
2) reliable;
3) impossible;
4) * opposite.
3. A dice is rolled. Let's denote the events: A - "loss of 6 points", B - "loss of 4 points", D - "loss of 2 points", C - "loss of an even number of points". Then the event C is
1)
 ;
;
2)
 ;
;
3)* ;
;
4)
 .
.
4. The student must pass two exams. Event A - "the student passed the first exam", event B - "the student passed the second exam", event C - "the student passed both exams". Then the event C is
1)* ;
;
2)
 ;
;
3)
 ;
;
4)
 .
.
5. From the letters of the word "TASK" one letter is randomly selected. The event - "the letter K is selected" is
1) random;
2) reliable;
3)* impossible;
4) opposite.
6. From the letters of the word "WORLD" one letter is randomly selected. The event - "the letter M is selected" is
1)* random;
2) reliable;
3) impossible.
7. The event - "a white ball is drawn from an urn containing only white balls" is
1) random;
2) * reliable;
3) impossible.
8. Two students take an exam. Events: A - "the first student will pass the exam", B - "the second student will pass the exam" are
1) incompatible;
2) reliable;
3) impossible;
4)*joint.
9. Events are called incompatible if
4) * the onset of one excludes the possibility of the appearance of the other.
10. Events are called the only possible ones if
1) the occurrence of one does not exclude the possibility of the appearance of another;
2) in the implementation of a set of conditions, each of them has an equal opportunity to occur;
3) * during the test, at least one of them will definitely occur;
Topic 2. Classical definition of probability
Basic concepts on the topic:
1. The probability of an event, the classical definition of the probability of a random event.
2. An outcome favorable to the event.
3. Geometric definition of probability.
4. Relative frequency of the event.
5. Statistical definition of probability.
6. Properties of probability.
7. Methods for counting the number of elementary outcomes: permutations, combinations, placements.
Application of all these concepts on practical examples.
Sample test tasks offered in this topic:
1. Events are called equally likely if
1) they are incompatible;
2) * in the implementation of a set of conditions, each of them has an equal opportunity to occur;
3) during the test, at least one of them will definitely occur;
4) the occurrence of one excludes the possibility of the appearance of the other.
2. Test - "throw two coins." Event - "at least one of the coins will have a coat of arms." The number of elementary outcomes that favor this event is equal to:
4) four.
3. Test - "throw two coins." Event - "a coat of arms will fall on one of the coins." The number of all elementary, equally possible, the only possible, incompatible outcomes is equal to:
4)* four.
4. There are 12 balls in the urn, they do not differ in anything except the color. Among these balls, 5 are black and 7 are white. The event is "a white ball is randomly drawn." For this event, the number of favorable outcomes is:
5. There are 12 balls in the urn, they do not differ in anything except the color. Among these balls, 5 are black and 7 are white. The event is "a white ball is randomly drawn." For this event, the number of all outcomes is:
6. The probability of an event takes any value from the interval:
3)
 ;
;
4)
 ;
;
5)* .
.
7. The subscriber forgot the last two digits of the telephone number and, knowing only that they are different, dialed them at random. In how many ways can he do this?
1) ;
;
2)* ;
;
1. Specify correct definition. The sum of two events is called:
a) A new event, consisting in the fact that both events occur at the same time;
b) A new event, consisting in the fact that either the first, or the second, or both occur; +
- Specify correct definition. The product of two events is called:
a) A new event, consisting in the fact that both events occur at the same time;+
b) A new event, consisting in the fact that either the first or the second occurs, or both together;
c) A new event, consisting in the fact that one thing happens but another does not happen.
- Specify correct definition. The probability of an event is:
a) The product of the number of outcomes that favor the occurrence of the event by the total number of outcomes;
b) The sum of the number of outcomes that favor the occurrence of the event and the total number of outcomes;
c) The ratio of the number of outcomes that favor the occurrence of an event to the total number of outcomes; +
- Specify correct statement. Probability of an impossible event:
b) equal to zero;+
c) is equal to one;
- Specify correct statement. Probability of certain event:
a) greater than zero and less than one;
b) equal to zero;
c) is equal to one;+
- Specify correct property. Probability of a random event:
a) greater than zero and less than one; +
b) equal to zero;
c) is equal to one;
- Specify correct statement:
a) The probability of the sum of events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events;
b) The probability of the sum of independent events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events;
c) The probability of the sum of incompatible events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events; +
- Specify correct statement:
a) The probability of producing events is equal to the product of the probabilities of these events;
b) The probability of producing independent events is equal to the product of the probabilities of these events; +
c) The probability of producing incompatible events is equal to the product of the probabilities of these events;
- Specify correct definition.Event is:
a) Elementary outcome;
b) The space of elementary outcomes;
c) A subset of the set of elementary outcomes.+
- Specify correct answer. What events are called hypotheses?
a) any pairwise incompatible events;
b) pairwise incompatible events, the combination of which forms a reliable event; +
c) the space of elementary events.
- Specify correct Answer Bayes formulas define:
a) prior probability of the hypothesis,
b) the posterior probability of the hypothesis,
c) the probability of the hypothesis.+
- Specify correct property. distribution function random variable X is:
a) non-increasing; b) non-decreasing; +c) arbitrary form.
- Specify correct
a) independent +; b) dependent; c) everyone.
- Specify correct property. The equality is valid for random variables:
a) independent; + b) dependent; c) everyone.
- Specify correct conclusion. From the fact that the correlation moment for two random variables X and Y zero follows:
a) there is no functional relationship between X and Y;
b) X and Y are independent;+
c) there is no linear correlation between X and Y;
- Specify correct answer. A discrete random variable is given by:
a) indicating its probabilities;
b) indicating its distribution law;+
c) putting each elementary outcome in correspondence
real number.
- Specify correct definition. The mathematical expectation of a random variable is:
a) the initial moment of the first order;+
b) the central moment of the first order;
c) an arbitrary moment of the first order.
- Specify correct definition. The variance of a random variable is:
a) the initial moment of the second order;
b) second-order central moment;+
c) an arbitrary moment of the second order.
- Specify faithful formula. The formula for calculating the standard deviation of a random variable:
a) +; b) ; V) .
- Specify correct definition. The distribution mode is:
a) the value of a random variable at which the probability is 0.5;
b) the value of a random variable at which either the probability or the density function reaches its maximum value;+
c) the value of a random variable at which the probability is 0.
- Specify faithful formula. The dispersion of a random variable is calculated by the formula:
- Specify faithful formula. The density of the normal distribution of a random variable is determined by the formula:
- Specify correct answer Mathematical expectation of a random variable distributed over normal law distribution is equal to:
- Specify correct answer. The mathematical expectation of a random variable distributed according to the exponential distribution law is:
- Specify correct answer. The variance of a random variable distributed according to the exponential distribution law is equal to:
- Specify faithful formula. For a uniform distribution, the mathematical expectation is determined by the formula:
- Specify faithful formula. For a uniform distribution, the dispersion is determined by the formula:
- Specify wrong statement. Sample variance properties:
a) if all options are increased by the same number of times, then the variance will increase by the same number of times.
b) the variance of the constant is zero.
c) if all options are increased by the same number, then the sample variance will not change.+
- Specify correct statement. Parameter estimation is called:
a) Representation of observations as independent random variables with the same distribution law.
b) the totality of the results of observations;
c) any function of the results of observation.+
- Specify correct statement. Distribution parameter estimates have the following property:
a) unbiased;+
b) significance;
c) importance.
- Specify not correct statement.
a) The maximum likelihood method is used to obtain estimates;
b) The sample variance is a biased estimate for the variance;
c) Unbiased, inconsistent, effective estimates are used as statistical estimates of parameters.+
- Specify wrong statement. The following properties are true for the distribution function of a two-dimensional random variable:
A) ; b) ; c) +.
- Specify wrong statement:
a) One-dimensional (marginal) distributions of individual components can always be found from a multidimensional distribution function.
b) One-dimensional (marginal) distributions of individual components can always be used to find a multidimensional distribution function.
c) One-dimensional (marginal) distribution densities of individual components can always be found from a multidimensional density function.
- Specify correct statement. The variance of the difference of two random variables is determined by the formula:
A); b)+; V) .
- Specify wrong statement. Joint Density Formula:
- Specify wrong statement. Random variables X and Y are called independent if:
a) The distribution law of the random variable X does not depend on the value of the random variable Y.
c) the correlation coefficient between the random variables X and Y is equal to zero.
- Specify correct answer. The formula is:
a) an analogue of the Bayes formula for continuous random variables;
b) an analog of the total probability formula for continuous random variables;+
c) an analogue of the formula for the product of the probabilities of independent events for continuous random variables.
- Specify wrong definition:
a) The initial moment of the order of a two-dimensional random variable (X, Y) is the expectation of the product by, i.e.
b) The central moment of the order of a two-dimensional random variable (X,Y) is the mathematical expectation of the product centered on, i.e.)
c) The correlation moment of a two-dimensional random variable (X, Y) is the mathematical expectation of the product by, i.e. +
- Specify correct answer. The dispersion of a random variable distributed according to the normal distribution law is equal to:
- Specify wrong statement. The simplest tasks of mathematical statistics are:
a) sampling and grouping of statistical data obtained as a result of the experiment;
b) determination of distribution parameters, the form of which is known in advance;
c) obtaining an estimate of the probability of the event under study.
1 option
1. The experiment was performed n times, the event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n=m=100
2. They threw a dice. What is the probability of getting an even number of points?
Answer:
1 2 – 2nd part is defective, A 3 – The 3rd part is defective. Record event: B - all parts are defective.
Answer:
- the -th boiler is working ( =1,2,3). Record event: unit is running The machine-boiler unit is running if the machine and at least one boiler are running.
Answer:
5. An n-volume collected works were placed on the shelf in random order. What is the probability that the books are in ascending order of volume numbers if n = 5.
Answer:
6. There are 8 girls and 6 boys in the group. They were divided into two equal subgroups. How many outcomes favor the event: all the boys will be in the same subgroup?
7. A coin was flipped 3 times. What is the probability that heads will come up 3 times.
Answers:
8. There are 25 balls in a box, of which 10 are white, 7 are blue, 3 are yellow, and 5 are blue. Find the probability that a randomly drawn ball is white.
Answers:
9. Choose the correct answer:
Answers:
10. Choose the correct answer: Total probability formula
11. Find P (AB) if
Answers:
12. Find if P(A) = 0.2
13. Events A and B are incompatible. Find P(A + B) if P(A) = P(B) = 0.3
14. Find P (A + B) if P (A) \u003d P (B) \u003d 0.3 P (AB) \u003d 0.1
15. The experience was made n times. Event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n = 10, m = 2
16. The most probable number of occurrences of an event when repeating tests is found by the formula:
17. The sum of the products of each DSV value and the corresponding probability is called.
p = 0.9; n = 10
p = 0.9; n = 10
22. . The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find P(x
23. Find the appropriate formula: M(x) =?
Answers:
Find .
Answers:
Answers:
27. A random variable has a uniform distribution if
Answers:
Answers:
Answer: a) b)
c) d)
30. In formula
Answers:
Test on the subject "Theory of Probability and math statistics»
Option 2
1. The experiment was performed n times, the event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n=1000; m=100
Answer: a) 0.75 b) 1 c) 0.5 d) 0.1
2. They threw a dice. What is the probability of getting more than four
Answer:
3. There are 20 standard parts and 7 defective parts in a box. Pulled out three parts. Event A 1 – 1st part is defective, A 2 – 2nd part is defective, A 3 – The 3rd part is defective. Record event: B - all parts are standard.
Answer:
4. Let A - the machine works, B- the -th boiler is working ( =1,2,3). Record event: unit is running The machine-boiler unit is running if the machine and at least two boilers are running.
Answer:
5. An n-volume collected works were placed on the shelf in random order. What is the probability that the books are in ascending order of volume numbers if n = 8.
Answer:
6. There are 8 girls and 6 boys in the group. They were divided into two equal subgroups. How many outcomes favor the event: 2 young men will be in one subgroup, and 4 in another?
Answers a) 8 b) 168 c) 840 d) 56
7. A coin was flipped 3 times. What is the probability that heads will come up once.
Answers:
8. There are 25 balls in a box, of which 10 are white, 7 are blue, 3 are yellow, and 5 are blue. Find the probability that a randomly drawn ball is blue.
Answers:
9. Choose the correct answer:
Answers:
10. Choose the correct answer: Bernoulli formula
11. Find P (AB) if
Answers:
12. Find if P(A) = 0.8
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.8 c) 0.2 d) 0.6
13. Events A and B are incompatible. Find P(A + B) if P(A) = 0.25 P(B) = 0.45
Answers: a) 0.9 b) 0.8 c) 0.7 d) 0.6
14. Find P (A + B) if P (A) \u003d 0.2 P (B) \u003d 0.8 P (AB) \u003d 0.1
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.6 c) 0.9 d) 0.7
15. The experience was made n times. Event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n = 20, m = 3
Answers: a) b) 0.2 c) 0.25 d) 0.15
16. Local Moivre-Laplace theorem
17. The mathematical expectation of the square of the difference between the random variable X and its mathematical expectation is called:
Answers: a) the variance of a random variable b) the mathematical expectation of the DSV
C) standard deviation d) DSV distribution law
18. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find M(x).
p = 0.8; n = 9
Answers: a) 8.4 b) 6 c) 7.2 d) 9
19. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find D(x).
p = 0.8; n = 9
Answers: a) 2.52 b) 3.6 c) 1.44 d) 0.9
20. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answers: a) 2.8 b) 1.2 c) 2.4 d) 0.8
21. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find D(x).
Answers: a) 0.96 b) 0.64 c) 0.36 d) 0.84
22. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find P (x > 2).
Answers: a) 0.0272 b) 0.0272 c) 0.3398 d) 0.1792
23. Find the appropriate formula: D (x) \u003d?
Answers:
24. The law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answer: a) 3.8 b) 4.2 c) 0.7 d) 1.9
25. The law of distribution of DSV is set. Find.
Answers:
Answers:
27. A random variable has normal distribution, If
Answers:
28. Find differential function distribution f(x), if
Answers:
29. Find the integral distribution function F(x) if
Answer: a) b)
c) d)
30. In formula
Answers:
Test on the subject "Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics"
3 option
1. The experiment was performed n times, the event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n=500 m=255
Answer: a) 0.75 b) 1 c) 0.5 d) 0.1
2. They threw a dice. What is the probability of getting less than five
Answer:
3. There are 20 standard parts and 7 defective parts in a box. Pulled out three parts. Event A 1 – 1st part is defective, A 2 – 2nd part is defective, A 3 – The 3rd part is defective. Record event: B - at least one part is defective.
Answer:
4. Let A be a machine, B- the -th boiler is working ( =1,2,3). Record event: unit is running The machine-boiler unit is running if the machine and all boilers are running.
Answer:
5. An n-volume collected works were placed on the shelf in random order. What is the probability that there are 100 booksyat in ascending order of volume numbers if n = 10.
Answer:
6. There are 8 girls and 6 boys in the group. They were divided into two equal subgroups. How many outcomes favor the event: 3 young men will be in one subgroup, and 3 in another?
Answers a) 8 b) 168 c) 840 d) 56
7. A coin was flipped 3 times. What is the probability that heads will come up at least once.
Answers:
8. There are 25 balls in a box, of which 10 are white, 7 are blue, 3 are yellow, and 5 are blue. Find the probability that a randomly drawn ball is yellow.
Answers:
9. Choose the correct answer:
Answers:
10. Choose the correct answer: Bayss formula
11. Find P (AB) if
Answers:
12. Find if P(A) = 0.5
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.8 c) 0.2 d) 0.6
13. Events A and B are incompatible. Find P(A + B) if P(A) = 0.7 P(B) = 0.1
Answers: a) 0.9 b) 0.8 c) 0.7 d) 0.6
14. Find P (A + B) if P (A) \u003d 0.5 P (B) \u003d 0.2 P (AB) \u003d 0.1
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.6 c) 0.9 d) 0.7
15. The experience was made n times. Event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n = 40, m = 10
Answers: a) b) 0.2 c) 0.25 d) 0.15
16. Laplace integral theorem
17. The square root of the dispersion of a random variable is called:
Answers: a) the variance of a random variable b) the mathematical expectation of the DSV
C) standard deviation d) DSV distribution law
18. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find M(x).
p = 0.7; n = 12
Answers: a) 8.4 b) 6 c) 7.2 d) 9
19. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find D(x).
p = 0.7; n = 12
Answers: a) 2.52 b) 3.6 c) 1.44 d) 0.9
20. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answers: a) 2.8 b) 1.2 c) 2.4 d) 0.8
21. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find D(x).
Answers: a) 0.96 b) 0.64 c) 0.36 d) 0.84
22. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find P(0
Answers: a) 0.0272 b) 0.0272 c) 0.3398 d) 0.1792
(x) = ?
Answers:
24. The law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answer: a) 3.8 b) 4.2 c) 0.7 d) 1.9
25. The law of distribution of DSV is set. Find
Answers:
Answers:
27. A random variable has an exponential distribution if
Answers:
28. Find the differential distribution function f(x)if
Answers:
29. Find the integral distribution function F(x) if
Answer: a) b)
c) d)
30. In formula
Answers:
Test on the subject "Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics"
4 option
1. The experiment was performed n times, the event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n=400 m=300
Answer: a) 0.75 b) 1 c) 0.5 d) 0.1
2. They threw a dice. What is the probability of getting less than six
Answer:
3. There are 20 standard parts and 7 defective parts in a box. Pulled out three parts. Event A 1 – 1st part is defective, A 2 – 2nd part is defective, A 3 – The 3rd part is defective. Record event: B - one part is defective and two are standard.
Answer:
4. Let A be a machine, B- the -th boiler is working ( =1,2,3). Log an event: the unit is running the machine-boiler unit is running if the machine is running; 1st boiler and at least one of the other two boilers.
Answer:
5. An n-volume collected works were placed on the shelf in random order. What is the probability that the books are in ascending order of volume numbers if n = 7.
Answer:
6. There are 8 girls and 6 boys in the group. They were divided into two equal subgroups. How many outcomes favor the event: 5 young men will be in one subgroup, and 1 in another?
Answers a) 8 b) 168 c) 840 d) 56
7. A coin was flipped 3 times. What is the probability that heads will come up more than once.
Answers:
8. There are 25 balls in a box, of which 10 are white, 7 are blue, 3 are yellow, and 5 are blue. Find the probability that a randomly drawn ball is blue.
Answers:
9. Choose the correct answer:
Answers:
10. Choose the correct answer: The formula for the product of the probabilities of dependent events
11. Find P (AB) if
Answers:
12. Find if P(A) = 0.4
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.8 c) 0.2 d) 0.6
13. Events A and B are incompatible. Find P(A + B) if P(A) = 0.6 P(B) = 0.3
Answers: a) 0.9 b) 0.8 c) 0.7 d) 0.6
14. Find P (A + B) if P (A) \u003d 0.6 P (B) \u003d 0.4 P (AB) \u003d 0.4
Answers: a) 0.5 b) 0.6 c) 0.9 d) 0.7
15. The experience was made n times. Event A happened m times. Find the frequency of occurrence of event A: n = 60, m = 10
Answers: a) b) 0.2 c) 0.25 d) 0.15
16. Bernoulli's theorem
17. A correspondence that establishes a connection between the possible values of a random variable and their probabilities is called:
Answers: a) the variance of a random variable b) the mathematical expectation of the DSV
C) standard deviation d) DSV distribution law
18. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find M(x).
p = 0.6; n = 10
Answers: a) 8.4 b) 6 c) 7.2 d) 9
19. The probability of failure-free operation of one cell of the milking machine is p. X is the number of non-failure cells of the milking machine during the milking of n cows. Find D(x).
p = 0.6; n = 10
Answers: a) 2.52 b) 3.6 c) 1.44 d) 0.9
20. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answers: a) 2.8 b) 1.2 c) 2.4 d) 0.8
21. The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find D(x).
Answers: a) 0.96 b) 0.64 c) 0.36 d) 0.84
22. . The binomial law of distribution of DSV is given. Find P(1
Answers: a) 0.0272 b) 0.0272 c) 0.3398 d) 0.1792
23. Find the corresponding formula:
Answers:
24. The law of distribution of DSV is given. Find M(x).
Answer: a) 3.8 b) 4.2 c) 0.7 d) 1.9
25. The law of distribution of DSV is set. Find
Answers:
Answers:
27. A random variable has a binomial distribution if
Answers:
28. Find the differential distribution function f(x)if
Answers:
29. Find the integral distribution function F(x) if
Answer: a) b)
c) d)
30. In formula
Answers:
1. MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE SETTING THE REGULARITIES OF RANDOM PHENOMENA IS:
a) medical statistics
b) probability theory
c) medical demographics
d) higher mathematics
Correct answer: b
2. THE POSSIBILITY OF IMPLEMENTING ANY EVENT IS:
a) experiment
b) scheme of cases
c) regularity
d) probability
The correct answer is g
3. EXPERIMENT IS:
a) the process of accumulation of empirical knowledge
b) the process of measuring or observing an action in order to collect data
c) study covering the entire population of observation units
d) mathematical modeling of reality processes
Correct answer b
4. OUTCOME IN PROBABILITY THEORY IS UNDERSTANDING:
a) an uncertain result of the experiment
b) a certain result of the experiment
c) the dynamics of the probabilistic process
d) the ratio of the number of units of observation to the general population
Correct answer b
5. SAMPLE SPACE IN PROBABILITY THEORY IS:
a) the structure of the phenomenon
b) all possible outcomes of the experiment
c) the ratio between two independent sets
d) the ratio between two dependent populations
Correct answer b
6. A FACT WHICH MAY OCCUR OR NOT OCCUR IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF A CERTAIN COMPLEX OF CONDITIONS:
a) frequency of occurrence
b) probability
c) a phenomenon
d) an event
The correct answer is g
7. EVENTS THAT OCCUR WITH THE SAME FREQUENCY AND NONE OF THEM IS OBJECTIVELY MORE POSSIBLE THAN THE OTHERS:
a) random
b) equiprobable
c) equivalent
d) selective
Correct answer b
8. AN EVENT WHICH WILL NEED TO OCCUR IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS IS CONSIDERED:
a) necessary
b) expected
c) reliable
d) priority
Correct answer in
8. THE OPPOSITE OF A CREDIBLE EVENT IS AN EVENT:
a) unnecessary
b) unexpected
c) impossible
d) non-priority
Correct answer in
10. PROBABILITY OF A RANDOM EVENT:
a) greater than zero and less than one
b) more than one
c) less than zero
d) represented by whole numbers
Correct answer a
11. EVENTS FORM A COMPLETE GROUP OF EVENTS IF CERTAIN CONDITIONS ARE IMPLEMENTED, AT LEAST ONE OF THEM:
a) will always appear
b) will appear in 90% of experiments
c) will appear in 95% of experiments
d) will appear in 99% of experiments
Correct answer a
12. THE PROBABILITY OF THE APPEARANCE OF ANY EVENT FROM THE FULL GROUP OF EVENTS IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS IS EQUAL TO:
The correct answer is g
13. IF NO TWO EVENTS CAN APPEAR SIMULTANEOUSLY DURING THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS, THEY ARE CALLED:
a) credible
b) incompatible
c) random
d) probable
Correct answer b
14. IF NONE OF THE EVALUATED EVENTS IS OBJECTIVELY MORE POSSIBLE THAN THE OTHERS IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS, THEN THEY:
a) equal
b) joint
c) equally likely
d) incompatible
Correct answer in
15. A VALUE WHICH CAN TAKE DIFFERENT VALUES UNDER THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS IS CALLED:
a) random
b) equally possible
c) selective
d) total
Correct answer a
16. IF WE KNOW THE NUMBER OF POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF A SOME EVENT AND THE TOTAL NUMBER OF OUTCOMES IN THE SAMPLE SPACE, THEN WE CAN CALCULATE:
a) conditional probability
b) classical probability
c) empirical probability
d) subjective probability
Correct answer b
17. WHEN WE DO NOT HAVE ENOUGH INFORMATION ABOUT WHAT IS HAPPENING AND CANNOT DETERMINE THE NUMBER OF POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF THE EVENT OF INTEREST IN US, WE CAN CALCULATE:
a) conditional probability
b) classical probability
c) empirical probability
d) subjective probability
Correct answer in
18. BASED ON YOUR PERSONAL OBSERVATIONS, YOU DO:
a) objective probability
b) classical probability
c) empirical probability
d) subjective probability
The correct answer is g
19. THE SUM OF TWO EVENTS A AND IN THE EVENT IS CALLED:
a) consisting in the successive occurrence of either event A or event B, excluding their joint occurrence
b) consisting in the appearance of either event A or event B
c) consisting in the appearance of either event A, or event B, or events A and B together
d) consisting in the appearance of event A and event B together
Correct answer in
20. PRODUCTION OF TWO EVENTS A AND IN IS AN EVENT CONSISTING IN:
a) the joint occurrence of events A and B
b) consecutive appearance of events A and B
c) the appearance of either event A, or event B, or events A and B together
d) the occurrence of either event A or event B
Correct answer a
21. IF EVENT A DOES NOT AFFECT THE PROBABILITY OF AN EVENT IN, AND CONVERSE, THEY CAN BE CONSIDERED:
a) independent
b) ungrouped
c) remote
d) heterogeneous
Correct answer a
22. IF EVENT A AFFECTS THE PROBABILITY OF AN EVENT IN, AND CONVERSUS, THEY CAN BE COUNTERED:
a) homogeneous
b) grouped
c) one-time
d) dependent
The correct answer is g
23. PROBABILITY ADDITION THEOREM:
a) the probability of the sum of two joint events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events
b) the probability of the successive occurrence of two joint events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events
c) the probability of the sum of two incompatible events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events
d) the probability of non-occurrence of two incompatible events is equal to the sum of the probabilities of these events
Correct answer in
24. ACCORDING TO THE LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS, WHEN THE EXPERIMENT IS CARRIED OUT A LARGE NUMBER OF TIMES:
a) empirical probability tends to classical
b) the empirical probability moves away from the classical
c) subjective probability exceeds the classical one
d) the empirical probability does not change with respect to the classical
Correct answer a
25. PROBABILITY OF THE PRODUCT OF TWO EVENTS A AND IN IS EQUAL TO THE PRODUCT OF THE PROBABILITY OF ONE OF THEM ( A) ON THE CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY OF THE OTHER ( IN), CALCULATED UNDER THE CONDITION THAT THE FIRST OCCURRED:
a) probability multiplication theorem
b) probability addition theorem
c) Bayes' theorem
d) Bernoulli's theorem
Correct answer a
26. ONE OF THE CONSEQUENCES OF THE THEOREM OF PROBABILITY MULTIPLICATION:
b) if event A affects event B, then event B affects event A
d) if the event Ane affects the event B, then the event B does not affect the event A
Correct answer in
27. ONE OF THE CONSEQUENCES OF THE THEOREM OF PROBABILITY MULTIPLICATION:
a) if event A depends on event B, then event B depends on event A
b) the probability of producing independent events is equal to the product of the probabilities of these events
c) if event A does not depend on event B, then event B does not depend on event A
d) the probability of the product of dependent events is equal to the product of the probabilities of these events
Correct answer b
28. THE INITIAL PROBABILITIES OF THE HYPOTHESES BEFORE ADDITIONAL INFORMATION IS RECEIVED ARE CALLED
a) a priori
b) a posteriori
c) preliminary
d) initial
Correct answer a
29. PROBABILITIES REVISED AFTER ADDITIONAL INFORMATION IS REVIEWED ARE CALLED
a) a priori
b) a posteriori
c) preliminary
d) final
Correct answer b
30. WHAT THEOREM OF PROBABILITY THEORY CAN BE APPLIED IN THE DIAGNOSIS
a) Bernoulli
b) Bayesian
c) Chebyshev
d) Poisson
Correct answer b
A) !
B) 
b) 
G) P(A)= 
The order is not important when using
A) placements
B) permutations
B) combinations
D) permutations and placements

A) 12  13
13 14
14 15=32760
15=32760
B) 13  14
14 15=2730
15=2730
AT 12  13
13 14=2184
14=2184
D) 14  15=210
15=210
Combination of n elements by m-This
A) the number of subsets containingm elements
B) the number of place changes by an element of a given set
C) the number of ways to choosem elements from nc order
D) the number of ways to choosem elements from nregardless of order
How many ways are there to seat the quartet from the fable of the same name by I.A. Krylov?
A) 24
B) 4
AT 8
D) 6
In how many ways can one headman and one fizorg be chosen from a group of 30 people?
A) 30
B) 870
B) 435
D) 30!

A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 
B) ( m-2)(m-1)m
B) (m-1)m
G) ( m-2)(m-1)
In how many ways can a group of 30 send 5 people to run the college run?
A) 17100720
B) 142506
B) 120
D) 30!
The eight students shook hands. How many handshakes were there?
A) 40320
B) 28
C) 16
D) 64
How many ways can you choose 3 books out of 9 given?
A) 
B) 
C) R 9
D) 3P 9
There are 5 red and 3 white roses in a vase. In how many ways can 4 flowers be taken?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
There are 8 red and 3 white roses in a vase. In how many ways can you take 2 red and 1 white roses?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 110
B) 108
AT 12
D) 9
There are 38 branches in the mailbox. In how many ways can 35 identical cards be placed in a box so that each box contains at most one card?
A) 
B) 35!
IN) 
D) 38!
How many different permutations can be formed from the word "elephant"?
A) 6
B) 4
C) 24
D) 8
In how many ways can two items be selected from a box containing 10 items?
A) 10!
B) 90
C) 45
D) 100
How many different two-digit numbers can be formed from the numbers 1,2,3,4?
A) 16
B) 24
AT 12
D) 6
3 vouchers are allocated for 5 employees. In how many ways can they be distributed if all vouchers are different?
A) 10
B) 60
B) 125
D) 243

A) (6;+  )
)
B) (-  ;6)
;6)
B) (0; +  )
)
D) (0;6)
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 4
B) 3
AT 2
D) 5
Write down the formula the phrase "the number of combinations ofnelements of 3 to 5 times less than number combinations ofn+2 elements of 4 »
A) 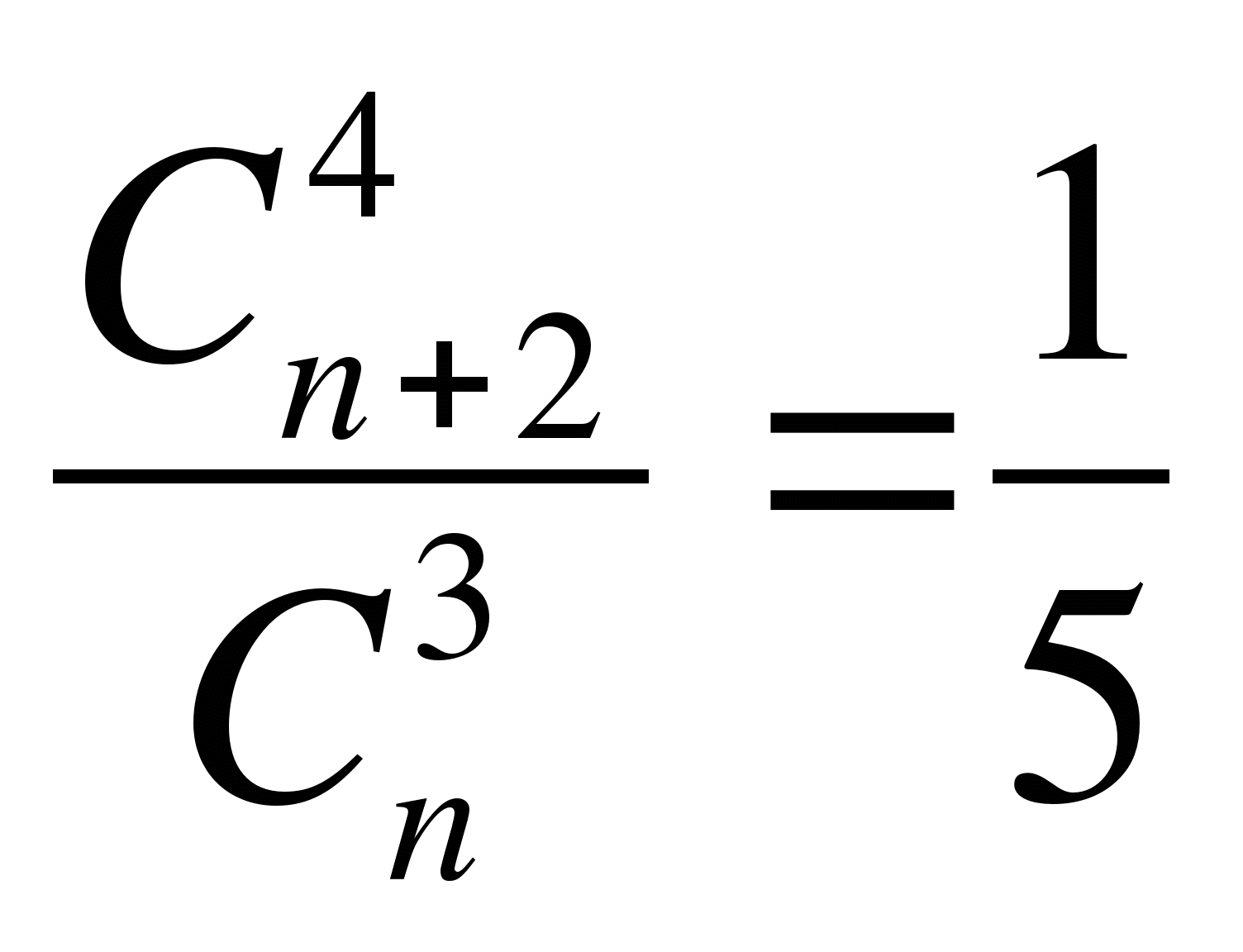
B) 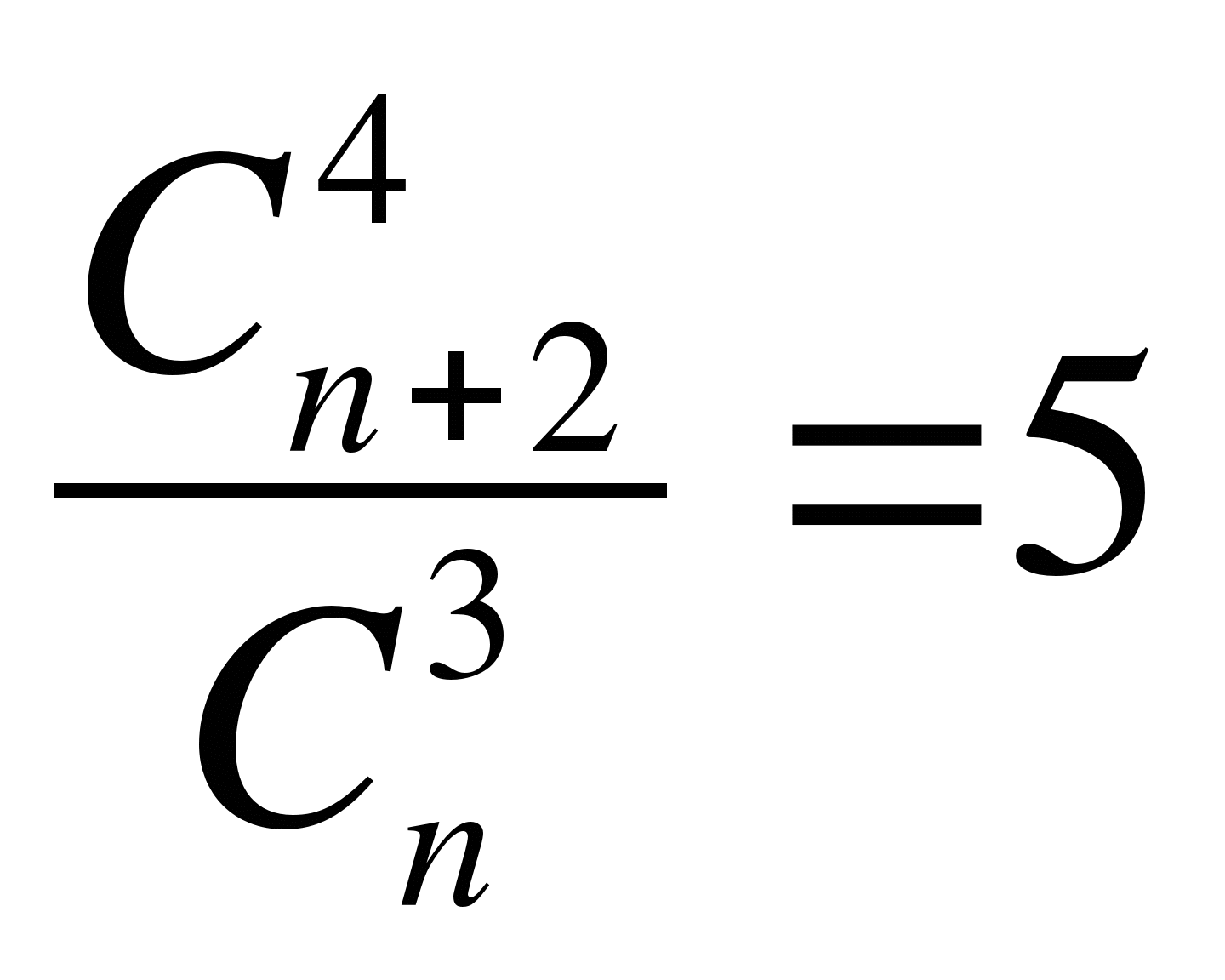
IN) 
G) 
In how many ways can 28 students be seated in a lecture hall?
A) 2880
B) 5600
C) 28!
D) 7200
In how many ways can 25 workers form teams of 5 people each?
A) 25!
B) 
IN) 
D) 125
There are 26 students in the group. In how many ways can 2 people be assigned to duty so that one of them is the leader?
A) 
B) 
C) 24!
D) 52

A) 6
B) 5
IN) 
D) 15
How many five-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4,5 without repetitions?
A) 24
B) 6
B) 120
D) 115
How many five-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4,5 so that 3 and 4 are side by side?
A) 120
B) 6
B) 117
D) 48
The Scientific Society consists of 25 members. It is necessary to choose the president of the society, the vice-president, the scientific secretary and the treasurer. In how many ways can this choice be made if each member of the society must hold only one position?
A) 303600
B) 25!
B) 506
D) 6375600

A) ( n-4)(n-5)
B) ( n-2)(n-1)n
IN) 
G) 

A) -2
B) -3
AT 2
D) 5
In how many ways can 8 rooks be placed on a chessboard so that they cannot attack each other?
A) 70
B) 1680
C) 64
D) 40320

A) 
B) (2 m-1)
IN) 2m
D) (2 m-2)!

A) ( n-5)!
B) 
IN) 
G) n(n-1)(n-2)

A) 6
B) 4
AT 5
D) 3

A) -1
B) 6
B) 27
D)-22

A) 1
B) 0
AT 3
D) 4

A) 9
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 0.3
The combination is calculated by the formula
A) !
B) 
B) P(A)= 
G) 
Accommodations are calculated using the formula
A) P(A)= 
B) 
b) 
G) !
Permutations from n elements is
A) the choice of elements from the set "n»
B) the number of elements in the set "n»
C) a subset of a set ofn elements
D) the established order in the set "n»
Placements are applied in the problem if
A) there is a choice of elements from the set, taking into account the order
B) there is a choice of elements from a set without regard to order
C) it is necessary to carry out a permutation in the set
D) if all selected elements are the same
An urn contains 6 white and 5 black balls. In how many ways can 2 white and 3 black balls be drawn from it?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
Among 100 lottery tickets, 45 are winning. In how many ways can one win out of three purchased tickets?
A) 45 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
Answers to test number 1
Answers to test number 2
Test #2
"Fundamentals of Probability Theory"
It's called a random event.
A) such an outcome of the experiment, in which the expected result may or may not occur
B) such an outcome of the experiment, which is already known in advance
C) an outcome of the experiment that cannot be determined in advance
D) such an outcome of the experiment, which, while maintaining the conditions of the experiment, is constantly repeated
conjunction "and" means
A) addition of probabilities of events
B) multiplying the probabilities of events
D) division of probabilities of events
conjunction "or" means
A) division of probabilities of events
B) addition of probabilities of events
C) the difference in the probabilities of events
D) multiplication of the probabilities of events
Events in which the occurrence of one precludes the occurrence of the other are called
A) incompatible
B) independent
B) dependent
D) joint
The complete group of events is formed by
A) a set of independent events, if as a result of single tests one of these events necessarily occurs
B) a set of independent events, if as a result of single tests all these events will necessarily occur
C) a set of incompatible events, if as a result of single tests one of these events necessarily occurs
D) a set of incompatible events, if as a result of single tests all these events will necessarily occur
The opposite are called
A) two independent, forming a complete group, events
B) two independent events
B) two incompatible events
D) two incompatible, forming a complete group, events
Two events are called independent
A) which as a result of the test will necessarily occur
B) which as a result of the test never occur together
C) in which the outcome of one of them does not depend on the outcome of the other event
D) in which the outcome of one of them is completely dependent on the outcome of another event
An event that is sure to occur as a result of the test
A) impossible
B) accurate
B) reliable
D) random
An event that will never happen as a result of the test
A) impossible
B) accurate
B) reliable
D) random
Highest value probabilities are
A) 100%
B) 1
B) infinity
D) 0
The sum of the probabilities of opposite events is equal to
A) 0
B) 100%
IN 1
D) 1
The phrase "at least one" means
A) only one element
B) not a single element
D) one, two or no more elements
The classical definition of probability
A) the probability of an event is the ratio of the number of outcomes that favor the occurrence of an event to the number of all incompatible, unique and equally possible outcomes that form a complete group of events.
B) Probability is a measure of the possibility of an event occurring in a particular test
C) Probability is the ratio of the number of trials in which an event occurred to the number of trials in which the event could or may not have occurred.
D) Each random event A from the field of events is assigned a non-negative number P(A), called probability.
Probability is a measure of the possibility of an event occurring in a particular test.
This is the definition of probability
A) classic
B) geometric
B) axiomatic
D) statistical
Probability is the ratio of the number of trials in which an event occurred to the number of trials in which the event might or might not have occurred. This is the definition of probability
A) classic
B) geometric
B) axiomatic
D) statistical
The conditional probability is calculated by the formula
A) P (A / B) \u003d 
B) P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B) -P (AB)
C) P (AB) \u003d P (A) P (B)
D) P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B)
This formula P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B) -P (AB) is used for two
A) incompatible events
B) joint events
B) dependent events
D) independent events
For which two events does the concept of conditional probability apply?
A) impossible
B) reliable
B) joint
D) dependent
Total Probability Formula
A) R( H I /A)=
B) P(A)=P(A/ H 1 ) P(H 1 )+ P(A/ H 2 ) P(H 2 )+…+ Р(А/ H n ) P(H n )
IN) P n (m)=
D) P(A)= 

B) Bayes' theorem
B) Bernoulli scheme
A) total probability formula
B) Bayes' theorem
B) Bernoulli scheme
D) classical definition of probability
Two dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of the rolled points is 6
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)=
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)=
Two dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of the rolled points is 11 and the difference is 5
A) P(A)=0
B) P(A)=2/36
C) P(A) = 1
D) P(A)=1/6
The device, which operates during the day, consists of three nodes, each of which, independently of the others, can fail during this time. Failure of any of the nodes disables the entire device. The probability of correct operation during the day of the first node is 0.9, the second - 0.85, the third - 0.95. What is the probability that the device will work during the day without fail?
A) P(A)=0.1 0.15 0.05=0.00075
B) P(A)=0.9 0.85 0.95=0.727
C) P(A)=0.1+0.85 0.95=0.91
D) P(A)=0.1 0.15 0.95=0.014
A two-digit number is conceived, the digits of which are different. Find the probability that a randomly named two-digit number will be equal to the intended number?
A) P(A)=0.1
B) P(A)=2/90
C) P (A) \u003d 1/100
D) P(A)=0.9
Two people shoot at a target with the same probability of hitting 0.8. What is the probability of hitting the target?
A) P(A)=0.8 0.8=0.64
B) P(A)=1-0.2 0.2=0.96
C) P(A)=0.8 0.2+0.2 0.2=0.2
D) P(A)=1-0.8=0.2
Two students are looking for the book they need. The probability that the first student finds the book is 0.6, and the second is 0.7. What is the probability that only one of the students will find the right book?
A) P(A)=1-0.6 0.7=0.58
B) P(A)=1-0.4 0.3=0.88
C) P(A)=0.6 0.3+0.7 0.4=0.46
D) P(A)=0.6 0.7+0.3 0.4=0.54
From a deck of 32 cards, two cards are taken at random one after the other. Find the probability that two kings are drawn?
A) P(A)=0.012
B) P (A) \u003d 0.125
C) P(A)=0.0625
D) P(A)=0.031
Three shooters independently shoot at a target. The probability of hitting the target for the first shooter is 0.75, for the second 0.8, for the third 0.9. Find the probability that at least one shooter hits the target?
A) P (A) \u003d 0.25 0.2 0.1 \u003d 0.005
B) P(A)=0.75 0.8 0.9=0.54
C) P(A)=1-0.25 0.2 0.1=0.995
D) P(A)=1-0.75 0.8 0.9=0.46
There are 10 identical parts in a box, marked with numbers from #1 to #10. Randomly take 6 parts. Find the probability that part number 5 will be among the extracted parts?
A) P (A) \u003d 5/10 \u003d 0.2
B) P(A)= 
C) P (A) \u003d 1/10 \u003d 0.1
D) P(A)= 
Find the probability that among 4 products taken at random, 3 will be defective if there are 10 defective products in a batch of 100 products.
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
There are 10 whites and 8 Red roses. Two flowers are chosen at random. What is the probability of that. What are they different colors?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A) = 2/18
The probability of hitting the target with one shot is 1/8. What is the probability that out of 12 shots there will be no misses?
A) R 12 (12)=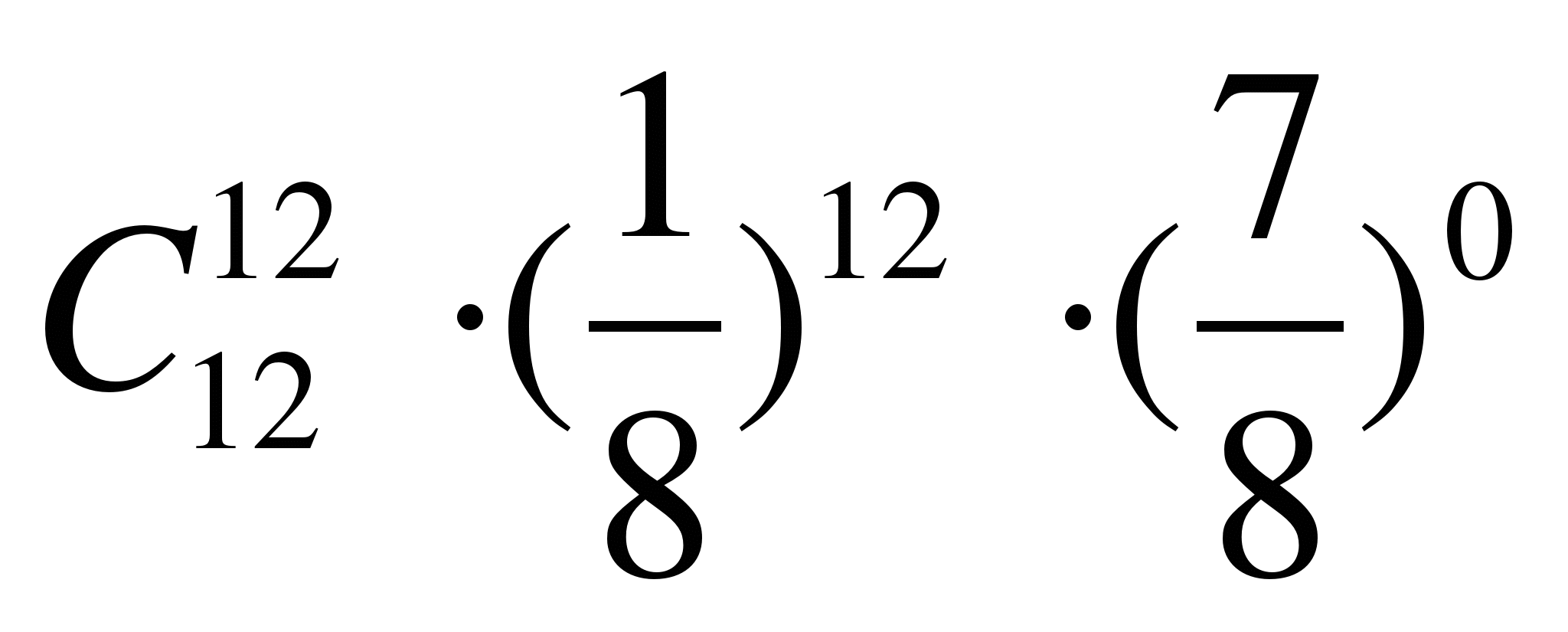
B) R 12 (1)=
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
The goalkeeper parries an average of 30% of all penalty kicks. What is the probability that he will take 2 out of 4 balls?
A) R 4 (2)=
B) R 4 (2)= 
C) R 4 (2)=
D) R 4 (2)= 
There are 40 vaccinated rabbits and 10 controls in the nursery. 14 rabbits are checked in a row, the result is recorded and the rabbits are sent back. Determine the most likely number of appearances of the control rabbit.
A) 10
B) 14
C) 14
D) 14
Top grade products at the shoe factory account for 10% of all production. How many pairs of top quality boots can you hope to find among the 75 pairs that came from this factory to the store?
A)75
B) 75
C) 75
D) 75

A) Local Laplace formula
B) Laplace integral formula
B) Moivre-Laplace formula
D) Bernoulli scheme
When solving the problem “The probability of the appearance of defects in a series of parts is 2%. What is the probability that in a batch of 600 parts there will be 20 defective ones? more applicable
A) Bernoulli scheme
B) De Moivre-Laplace formula
B) local Laplace formula
When solving the problem “In each of 700 independent tests for marriage, the appearance of a standard light bulb occurs with a constant probability of 0.65. Find the probability that, under these conditions, a defective light bulb will occur more often than in 230 trials, but less often than in 270 trials” is more applicable
A) Bernoulli scheme
B) De Moivre-Laplace formula
B) local Laplace formula
D) Laplace integral formula
When dialing a phone number, the subscriber forgot the number and dialed it at random. Find the probability that the desired number is dialed?
A) P(A)=1/9
B) P(A)=1/10
C) P(A)=1/99
D) P(A)=1/100
A dice is thrown. Find the probability of getting an even number of points?
A) P (A) \u003d 5/6
B) P(A)=1/6
C) P(A)=3/6
D) P(A)=1
There are 50 identical parts in a box, 5 of them are painted. One piece is drawn at random. Find the probability that the extracted part will be painted?
A) P(A)=0.1
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)=0.3
An urn contains 3 white and 9 black balls. Two balls are taken out of the urn at the same time. What is the probability that both balls are white?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
C) P(A)=2/12
D) P(A)= 
10 different books are placed at random on one shelf. Find the probability that 3 certain books will be placed side by side?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P (A) \u003d
D) P(A)= 
Participants in the draw draw tokens with numbers from 1 to 100 from the box. Find the probability that the number of the first randomly drawn token does not contain the number 5?
A) P(A)=5/100
B) P(A)=1/100
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
Test #3
"Discrete Random Variables"
A quantity that, depending on the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values, is called
A) random
B) discrete
B) continuous
D) probability
A discrete random variable is called
A) a value that, depending on the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values
B) a value that changes from one test to another with a certain probability
C) a value that does not change during several tests
D) a value that, regardless of the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values
Fashion is called
A) the average value of a discrete random variable
B) the sum of the products of the values of a random variable by their probability
C) the mathematical expectation of the square of the deviation of a value from its mathematical expectation
D) the value of a discrete random variable, the probability of which is the greatest
The mean value of a discrete random variable is called
A) fashion
B) mathematical expectation
B) median
The sum of the products of the values of a random variable and their probability is called
A) variance
B) mathematical expectation
B) fashion
D) standard deviation
Mathematical expectation of the squared deviation of a value from its mathematical expectation
A) fashion
B) median
B) standard deviation
D) dispersion
The formula by which the variance is calculated
A) 
B) M (x 2) -M (x)
C) M (x 2) - (M (x)) 2
D) (M (x)) 2 -M (x 2)
The formula by which the mathematical expectation is calculated
A) 
B) M (x 2) - (M (x)) 2
IN) 
G) 
For a given series of distribution of a discrete random variable, find the mathematical expectation
B) 1.3
B) 0.5
D) 0.8
For a given series of distribution of a discrete random variable, find M(x 2 )
B) 2.25
B) 2.9
D) 0.99
Find unknown probability
B) 0.75
C) 0
D) 1
Find fashion
B) 1.7
C) 0.28
D) 1.2
Find Median
B) 1.2
AT 4
D) 0.28
Find Median
B) 3.5
B) 0.25
D) 1.1
Find the unknown value of x if M(x)=1.1
B) 1.1
B) 1.2
D) 0
The mathematical expectation of a constant value is








