A) !
B) 
b) 
G) P(A)= 
The order is not important when using
A) placements
B) permutations
B) combinations
D) permutations and placements

A) 12  13
13 14
14 15=32760
15=32760
B) 13  14
14 15=2730
15=2730
AT 12  13
13 14=2184
14=2184
D) 14  15=210
15=210
Combination of n elements by m-This
A) the number of subsets containingm elements
B) the number of place changes by an element of a given set
C) the number of ways to choosem elements from nc order
D) the number of ways to choosem elements from nregardless of order
How many ways are there to seat the quartet from the fable of the same name by I.A. Krylov?
A) 24
B) 4
AT 8
D) 6
In how many ways can one headman and one fizorg be chosen from a group of 30 people?
A) 30
B) 870
B) 435
D) 30!

A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 
B) ( m-2)(m-1)m
B) (m-1)m
G) ( m-2)(m-1)
In how many ways can a group of 30 send 5 people to run the college run?
A) 17100720
B) 142506
B) 120
D) 30!
The eight students shook hands. How many handshakes were there?
A) 40320
B) 28
B) 16
D) 64
How many ways can you choose 3 books out of 9 given?
A) 
B) 
C) R 9
D) 3P 9
There are 5 red and 3 white roses in a vase. In how many ways can 4 flowers be taken?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
There are 8 red and 3 white roses in a vase. In how many ways can you take 2 red and 1 white roses?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 110
B) 108
AT 12
D) 9
There are 38 branches in the mailbox. In how many ways can 35 identical cards be placed in a box so that each box contains at most one card?
A) 
B) 35!
IN) 
D) 38!
How many different permutations can be formed from the word "elephant"?
A) 6
B) 4
C) 24
D) 8
In how many ways can two items be selected from a box containing 10 items?
A) 10!
B) 90
C) 45
D) 100
How many different two-digit numbers can be formed from the numbers 1,2,3,4?
A) 16
B) 24
AT 12
D) 6
3 vouchers are allocated for 5 employees. In how many ways can they be distributed if all vouchers are different?
A) 10
B) 60
B) 125
D) 243
A) (6;+  )
)
B) (-  ;6)
;6)
B) (0; +  )
)
D) (0;6)
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 

A) 4
B) 3
AT 2
D) 5
Write down the formula the phrase "the number of combinations ofnelements of 3 to 5 times less than number combinations ofn+2 elements of 4 »
A) 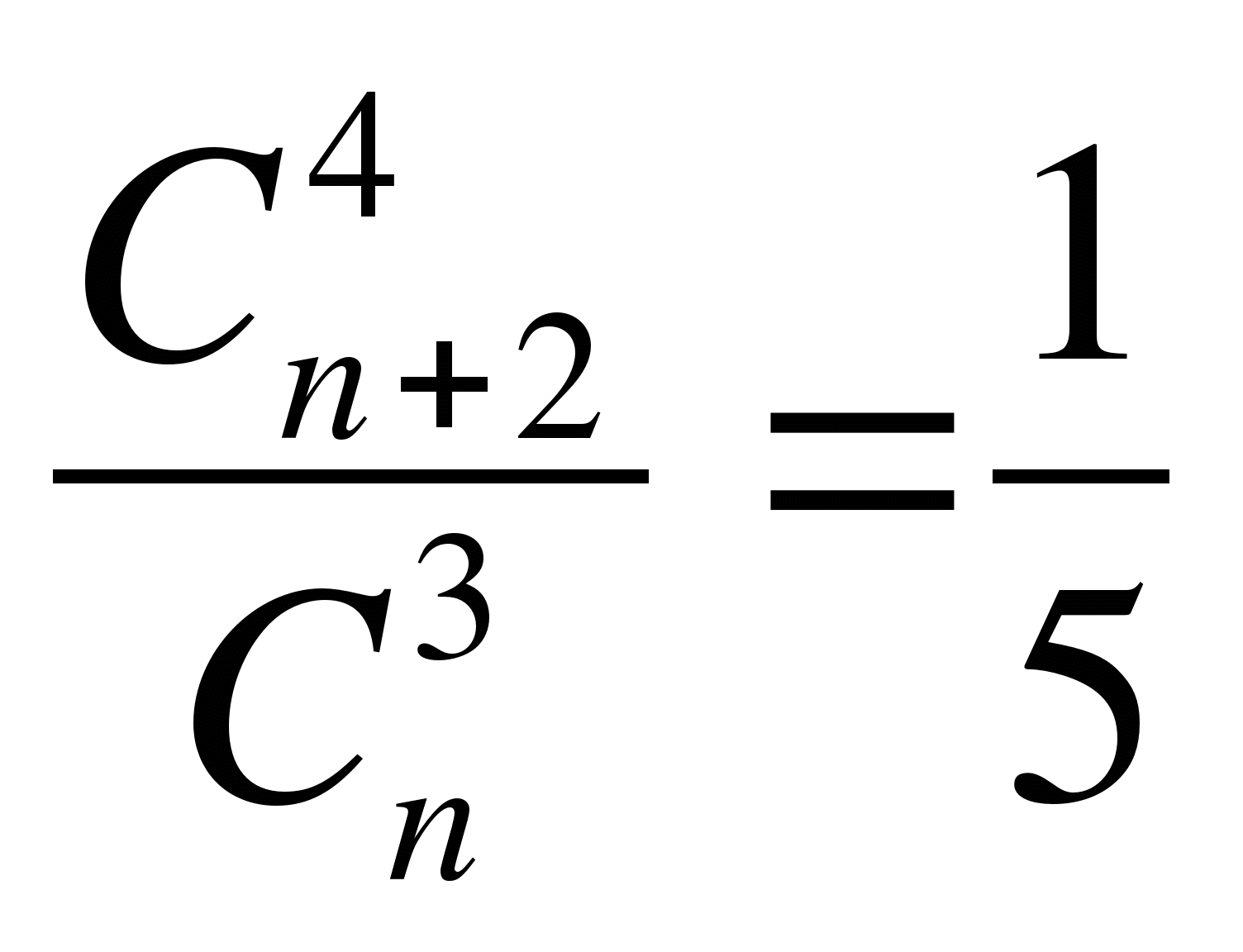
B) 
IN) 
G) 
In how many ways can 28 students be seated in a lecture hall?
A) 2880
B) 5600
C) 28!
D) 7200
In how many ways can 25 workers form teams of 5 people each?
A) 25!
B) 
IN) 
D) 125
There are 26 students in the group. In how many ways can 2 people be assigned to duty so that one of them is the leader?
A) 
B) 
C) 24!
D) 52

A) 6
B) 5
IN) 
D) 15
How many five-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4,5 without repetitions?
A) 24
B) 6
B) 120
D) 115
How many five-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4,5 so that 3 and 4 are side by side?
A) 120
B) 6
B) 117
D) 48
The Scientific Society consists of 25 members. It is necessary to choose the president of the society, the vice-president, the scientific secretary and the treasurer. In how many ways can this choice be made if each member of the society must hold only one position?
A) 303600
B) 25!
B) 506
D) 6375600

A) ( n-4)(n-5)
B) ( n-2)(n-1)n
IN) 
G) 

A) -2
B) -3
AT 2
D) 5
In how many ways can 8 rooks be placed on a chessboard so that they cannot attack each other?
A) 70
B) 1680
C) 64
D) 40320

A) 
B) (2 m-1)
IN) 2m
D) (2 m-2)!

A) ( n-5)!
B) 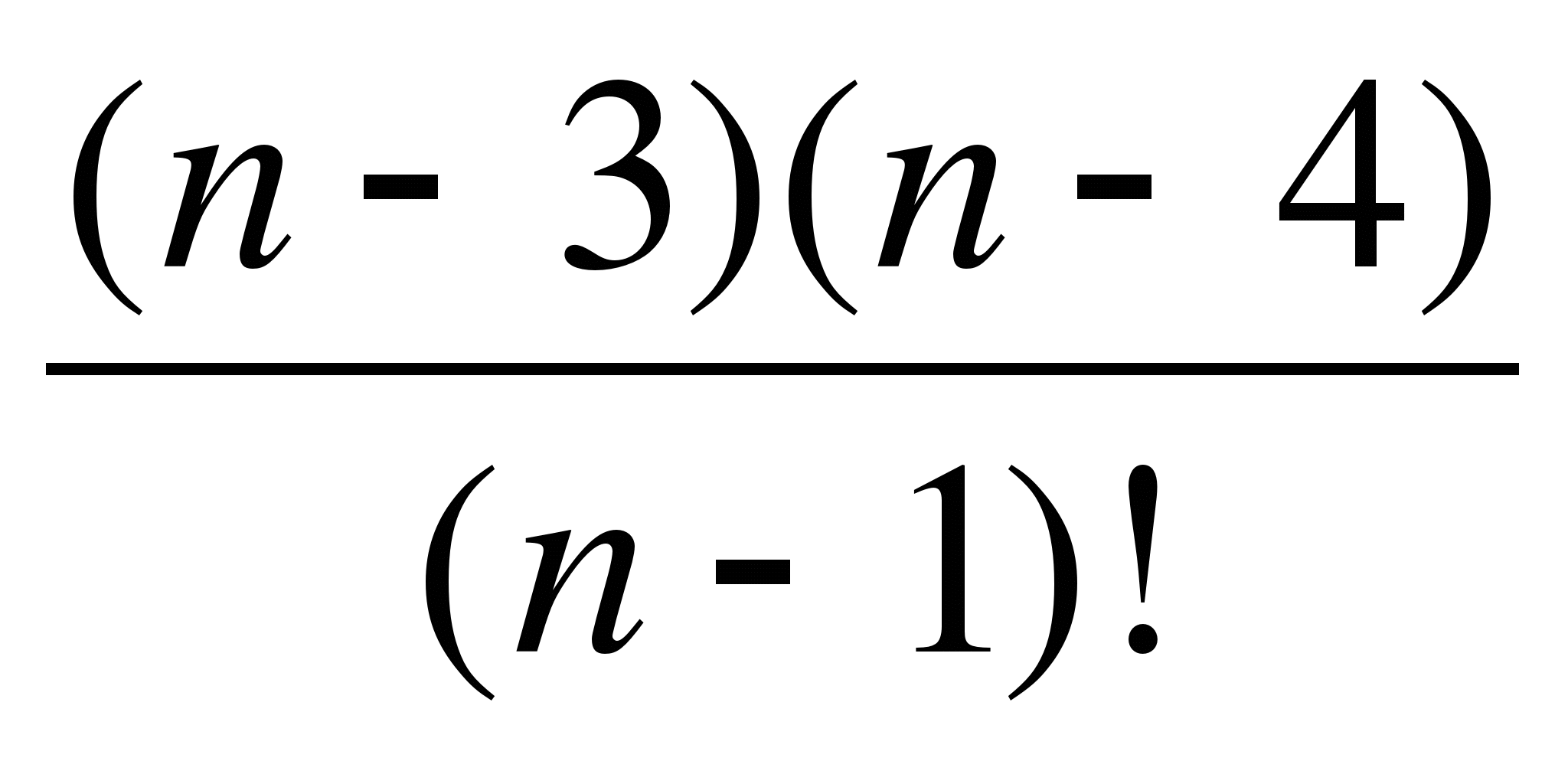
IN) 
G) n(n-1)(n-2)

A) 6
B) 4
AT 5
D) 3

A) -1
B) 6
C) 27
D)-22

A) 1
B) 0
AT 3
D) 4

A) 9
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 0.3
The combination is calculated by the formula
A) !
B) 
B) P(A)= 
G) 
Accommodations are calculated using the formula
A) P(A)= 
B) 
b) 
G) !
Permutations from n elements is
A) the choice of elements from the set "n»
B) the number of elements in the set "n»
C) a subset of a set ofn elements
D) the established order in the set "n»
Placements are applied in the problem if
A) there is a choice of elements from the set, taking into account the order
B) there is a choice of elements from a set without regard to order
C) it is necessary to carry out a permutation in the set
D) if all selected elements are the same
An urn contains 6 white and 5 black balls. In how many ways can 2 white and 3 black balls be drawn from it?
A) 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
Among 100 lottery tickets, 45 are winning. In how many ways can one win out of three purchased tickets?
A) 45 
B) 
IN) 
G) 
Answers to test number 1
Answers to test number 2
Test #2
"Fundamentals of Probability Theory"
It's called a random event.
A) such an outcome of the experiment, in which the expected result may or may not occur
B) such an outcome of the experiment, which is already known in advance
C) an outcome of the experiment that cannot be determined in advance
D) such an outcome of the experiment, which, while maintaining the conditions of the experiment, is constantly repeated
conjunction "and" means
A) addition of probabilities of events
B) multiplying the probabilities of events
D) division of probabilities of events
conjunction "or" means
A) division of probabilities of events
B) addition of probabilities of events
C) the difference in the probabilities of events
D) multiplication of the probabilities of events
Events in which the occurrence of one precludes the occurrence of the other are called
A) incompatible
B) independent
B) dependent
D) joint
The complete group of events is formed by
A) a set of independent events, if as a result of single tests one of these events necessarily occurs
B) a set of independent events, if as a result of single tests all these events will necessarily occur
C) a set of incompatible events, if as a result of single tests one of these events necessarily occurs
D) a set of incompatible events, if as a result of single tests all these events will necessarily occur
The opposite are called
A) two independent, forming a complete group, events
B) two independent events
B) two incompatible events
D) two incompatible, forming a complete group, events
Two events are called independent
A) which as a result of the test will necessarily occur
B) which as a result of the test never occur together
C) in which the outcome of one of them does not depend on the outcome of the other event
D) in which the outcome of one of them is completely dependent on the outcome of another event
An event that is sure to occur as a result of the test
A) impossible
B) accurate
B) reliable
D) random
An event that will never happen as a result of the test
A) impossible
B) accurate
B) reliable
D) random
Highest value probabilities are
A) 100%
B) 1
B) infinity
D) 0
The sum of the probabilities of opposite events is equal to
A) 0
B) 100%
IN 1
D) 1
The phrase "at least one" means
A) only one element
B) not a single element
D) one, two or no more elements
The classical definition of probability
A) the probability of an event is the ratio of the number of outcomes that favor the occurrence of an event to the number of all incompatible, unique and equally possible outcomes that form a complete group of events.
B) Probability is a measure of the possibility of an event occurring in a particular test
C) Probability is the ratio of the number of trials in which an event occurred to the number of trials in which the event could or may not have occurred.
D) Each random event A from the field of events is assigned a non-negative number P(A), called probability.
Probability is a measure of the possibility of an event occurring in a particular test.
This is the definition of probability
A) classic
B) geometric
B) axiomatic
D) statistical
Probability is the ratio of the number of trials in which an event occurred to the number of trials in which the event might or might not have occurred. This is the definition of probability
A) classic
B) geometric
B) axiomatic
D) statistical
The conditional probability is calculated by the formula
A) P (A / B) \u003d 
B) P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B) -P (AB)
C) P (AB) \u003d P (A) P (B)
D) P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B)
This formula P (A + B) \u003d P (A) + P (B) -P (AB) is used for two
A) incompatible events
B) joint events
B) dependent events
D) independent events
For which two events does the concept of conditional probability apply?
A) impossible
B) reliable
B) joint
D) dependent
Total Probability Formula
A) R( H I /A)=
B) P(A)=P(A/ H 1 ) P(H 1 )+ P(A/ H 2 ) P(H 2 )+…+ Р(А/ H n ) P(H n )
IN) P n (m)=
D) P(A)= 

B) Bayes' theorem
B) Bernoulli scheme
A) total probability formula
B) Bayes' theorem
B) Bernoulli scheme
D) classical definition of probability
Two dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of the rolled points is 6
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)=
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)=
Two dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of the rolled points is 11 and the difference is 5
A) P(A)=0
B) P(A)=2/36
C) P(A) = 1
D) P(A)=1/6
The device, which operates during the day, consists of three nodes, each of which, independently of the others, can fail during this time. Failure of any of the nodes disables the entire device. The probability of correct operation during the day of the first node is 0.9, the second - 0.85, the third - 0.95. What is the probability that the device will work during the day without fail?
A) P(A)=0.1 0.15 0.05=0.00075
B) P(A)=0.9 0.85 0.95=0.727
C) P(A)=0.1+0.85 0.95=0.91
D) P(A)=0.1 0.15 0.95=0.014
A two-digit number is conceived, the digits of which are different. Find the probability that a randomly named two-digit number will be equal to the intended number?
A) P(A)=0.1
B) P(A)=2/90
C) P (A) \u003d 1/100
D) P(A)=0.9
Two people shoot at a target with the same probability of hitting 0.8. What is the probability of hitting the target?
A) P(A)=0.8 0.8=0.64
B) P(A)=1-0.2 0.2=0.96
C) P(A)=0.8 0.2+0.2 0.2=0.2
D) P(A)=1-0.8=0.2
Two students are looking for the book they need. The probability that the first student finds the book is 0.6, and the second is 0.7. What is the probability that only one of the students will find the right book?
A) P(A)=1-0.6 0.7=0.58
B) P(A)=1-0.4 0.3=0.88
C) P(A)=0.6 0.3+0.7 0.4=0.46
D) P(A)=0.6 0.7+0.3 0.4=0.54
From a deck of 32 cards, two cards are taken at random one after the other. Find the probability that two kings are drawn?
A) P(A)=0.012
B) P (A) \u003d 0.125
C) P(A)=0.0625
D) P(A)=0.031
Three shooters independently shoot at a target. The probability of hitting the target for the first shooter is 0.75, for the second 0.8, for the third 0.9. Find the probability that at least one shooter hits the target?
A) P (A) \u003d 0.25 0.2 0.1 \u003d 0.005
B) P(A)=0.75 0.8 0.9=0.54
C) P(A)=1-0.25 0.2 0.1=0.995
D) P(A)=1-0.75 0.8 0.9=0.46
There are 10 identical parts in a box, marked with numbers from #1 to #10. Randomly take 6 parts. Find the probability that part number 5 will be among the extracted parts?
A) P (A) \u003d 5/10 \u003d 0.2
B) P(A)= 
C) P (A) \u003d 1/10 \u003d 0.1
D) P(A)= 
Find the probability that among 4 products taken at random, 3 will be defective if there are 10 defective products in a batch of 100 products.
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
There are 10 whites and 8 Red roses. Two flowers are chosen at random. What is the probability of that. What are they different colors?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A) = 2/18
The probability of hitting the target with one shot is 1/8. What is the probability that out of 12 shots there will be no misses?
A) R 12 (12)=
B) R 12 (1)=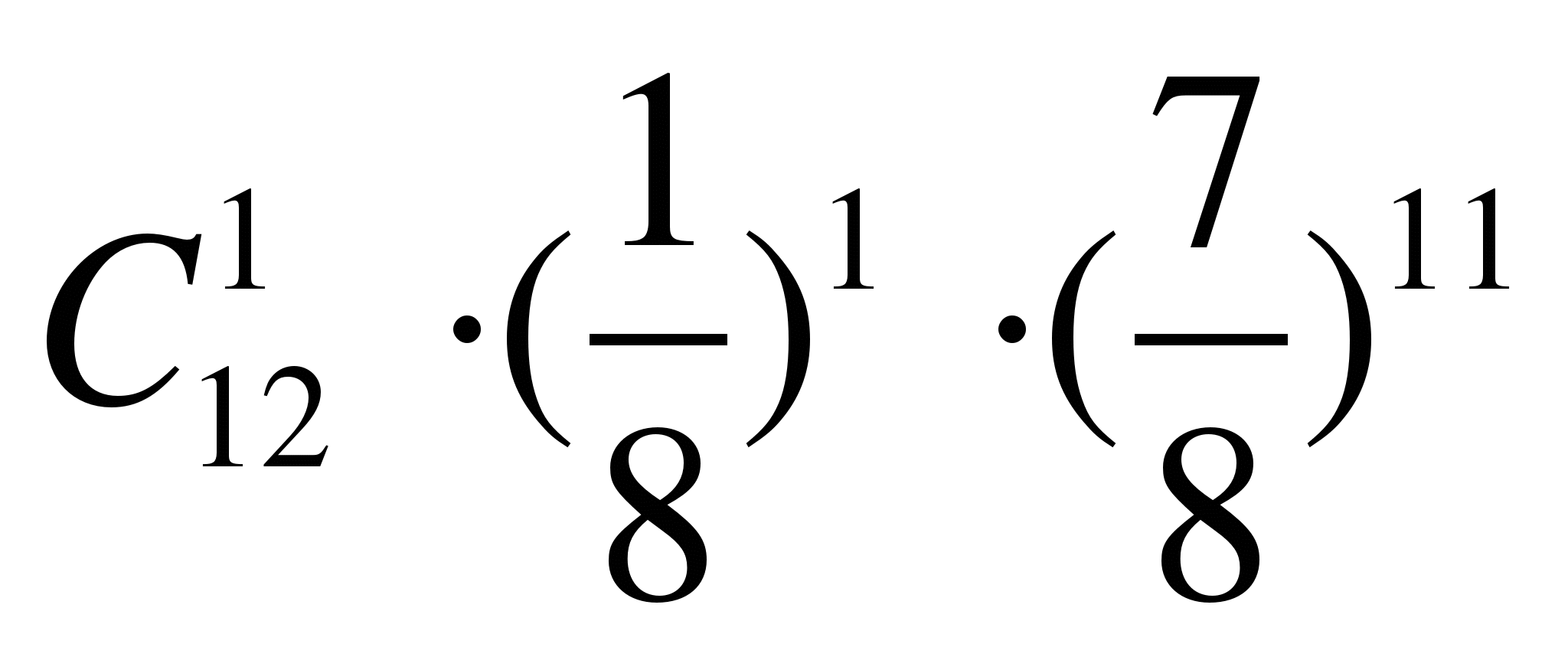
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
The goalkeeper parries an average of 30% of all penalty kicks. What is the probability that he will take 2 out of 4 balls?
A) R 4 (2)=
B) R 4 (2)= 
C) R 4 (2)=
D) R 4 (2)= 
There are 40 vaccinated rabbits and 10 controls in the nursery. 14 rabbits are checked in a row, the result is recorded and the rabbits are sent back. Determine the most likely number of appearances of the control rabbit.
A) 10
B) 14
C) 14
D) 14
Top grade products at the shoe factory account for 10% of all production. How many pairs of top quality boots can you hope to find among the 75 pairs that came from this factory to the store?
A)75
B) 75
C) 75
D) 75

A) Local Laplace formula
B) Laplace integral formula
B) Moivre-Laplace formula
D) Bernoulli scheme
When solving the problem “The probability of the appearance of defects in a series of parts is 2%. What is the probability that in a batch of 600 parts there will be 20 defective ones? more applicable
A) Bernoulli scheme
B) De Moivre-Laplace formula
B) local Laplace formula
When solving the problem “In each of 700 independent tests for marriage, the appearance of a standard light bulb occurs with a constant probability of 0.65. Find the probability that, under these conditions, a defective light bulb will occur more often than in 230 trials, but less often than in 270 trials” is more applicable
A) Bernoulli scheme
B) De Moivre-Laplace formula
B) local Laplace formula
D) Laplace integral formula
When dialing a phone number, the subscriber forgot the number and dialed it at random. Find the probability that the desired number is dialed?
A) P(A)=1/9
B) P(A)=1/10
C) P(A)=1/99
D) P(A)=1/100
A dice is thrown. Find the probability of getting an even number of points?
A) P (A) \u003d 5/6
B) P(A)=1/6
C) P(A)=3/6
D) P(A)=1
There are 50 identical parts in a box, 5 of them are painted. One piece is drawn at random. Find the probability that the extracted part will be painted?
A) P(A)=0.1
B) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)=0.3
An urn contains 3 white and 9 black balls. Two balls are taken out of the urn at the same time. What is the probability that both balls are white?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
C) P(A)=2/12
D) P(A)= 
10 different books are placed at random on one shelf. Find the probability that 3 certain books will be placed side by side?
A) P(A)= 
B) P(A)= 
B) P (A) \u003d
D) P(A)= 
Participants in the draw draw tokens with numbers from 1 to 100 from the box. Find the probability that the number of the first randomly drawn token does not contain the number 5?
A) P(A)=5/100
B) P(A)=1/100
B) P(A)= 
D) P(A)= 
Test #3
"Discrete random variables»
A quantity that, depending on the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values, is called
A) random
B) discrete
B) continuous
D) probability
A discrete random variable is called
A) a value that, depending on the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values
B) a value that changes from one test to another with a certain probability
C) a value that does not change during several tests
D) a value that, regardless of the result of the experiment, can take on different numerical values
Fashion is called
A) the average value of a discrete random variable
B) the sum of the products of the values of a random variable by their probability
C) the mathematical expectation of the square of the deviation of a value from its mathematical expectation
D) the value of a discrete random variable, the probability of which is the greatest
The mean value of a discrete random variable is called
A) fashion
B) mathematical expectation
B) median
The sum of the products of the values of a random variable and their probability is called
A) variance
B) mathematical expectation
B) fashion
D) standard deviation
Expected value the square of the deviation of a value from its mathematical expectation
A) fashion
B) median
B) standard deviation
D) dispersion
The formula by which the variance is calculated
A) 
B) M (x 2) -M (x)
C) M (x 2) - (M (x)) 2
D) (M (x)) 2 -M (x 2)
The formula by which the mathematical expectation is calculated
A) 
B) M (x 2) - (M (x)) 2
IN) 
G) 
For a given series of distribution of a discrete random variable, find the mathematical expectation
B) 1.3
B) 0.5
D) 0.8
For a given series of distribution of a discrete random variable, find M(x 2 )
B) 2.25
B) 2.9
D) 0.99
Find unknown probability
B) 0.75
C) 0
D) 1
Find fashion
B) 1.7
B) 0.28
D) 1.2
Find Median
B) 1.2
AT 4
D) 0.28
Find Median
B) 3.5
B) 0.25
D) 1.1
Find the unknown value of x if M(x)=1.1
B) 1.1
B) 1.2
D) 0
The mathematical expectation of a constant value is
OPTION 1
1. In a random experiment, two dice are thrown. Find the probability of getting 5 points in total. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
2. In a random experiment, a symmetrical coin is thrown three times. Find the probability that heads come up exactly twice.
3. On average, out of 1,400 garden pumps sold, 7 leak. Find the probability that one randomly selected pump does not leak.
4. The competition of performers is held in 3 days. There are 50 entries in total, one from each country. There are 34 performances on the first day, the rest are distributed equally among the remaining days. The order of performances is determined by a draw. What is the probability that the performance of the representative of Russia will take place on the third day of the competition?
5. The taxi company has 50 cars; 27 of them are black with yellow inscriptions on the sides, the rest are yellow with black inscriptions. Find the probability that a yellow car with black inscriptions will arrive at a random call.
6. Groups perform at the rock festival - one from each of the declared countries. The order of performance is determined by lot. What is the probability that a group from Germany will perform after a group from France and after a group from Russia? Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
7. What is the probability that a randomly selected natural number 41 to 56 is divisible by 2?
8. There are only 20 tickets in the collection of tickets in mathematics, 11 of them contain a question on logarithms. Find the probability that a student will get a logarithm question in a ticket randomly selected at the exam.
9. The figure shows a labyrinth. The spider crawls into the maze at the "Entrance" point. The spider cannot turn around and crawl back. At each fork, the spider chooses a path that has not yet crawled. Considering the choice of the further path as random, determine with what probability the spider will come to the exit.
10. To enter the institute for the specialty "Translator", the applicant must score at least 79 points on the Unified State Examination in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian and a foreign language. To enter the specialty "Customs", you need to score at least 79 points in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian language and social studies.
The probability that applicant B. will receive at least 79 points in mathematics is 0.9, in Russian - 0.7, in foreign language- 0.8 and in social studies - 0.9.
OPTION 2
1. There are three sellers in the store. Each of them is busy with a client with a probability of 0.3. Find the probability that at a random moment of time all three sellers are busy at the same time (assume that customers enter independently of each other).
2. In a random experiment, a symmetrical coin is tossed three times. Find the probability that the outcome of the RPP will come (all three times it comes up tails).
3. The factory produces bags. On average, for every 200 quality bags, there are four bags with hidden defects. Find the probability that the purchased bag will be of high quality. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
4. The competition of performers is held in 3 days. There are 55 entries in total, one from each country. There are 33 performances on the first day, the rest are distributed equally among the remaining days. The order of performances is determined by a draw. What is the probability that the performance of the representative of Russia will take place on the third day of the competition?
5. There are 10 digits on the telephone keypad, from 0 to 9. What is the probability that a randomly pressed number will be less than 4?
6. Biathlete shoots at targets 9 times. The probability of hitting the target with one shot is 0.8. Find the probability that the biathlete hit the targets the first 3 times and missed the last 6. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
7. Two factories produce the same glass for car headlights. The first factory produces 30 of these glasses, the second - 70. The first factory produces 4 defective glasses, and the second - 1. Find the probability that a glass randomly bought in a store will be defective.
8. There are only 25 tickets in the collection of chemistry tickets, 6 of them contain a question on hydrocarbons. Find the probability that a student will get a question on hydrocarbons in a ticket randomly selected in the exam.
9. In order to enter the institute for the specialty "Translator", the applicant must score at least 69 points on the Unified State Examination in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian and a foreign language. To enter the specialty "Management", you need to score at least 69 points in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian language and social studies.
The probability that applicant T. will receive at least 69 points in mathematics is 0.6, in Russian - 0.6, in a foreign language - 0.5 and in social studies - 0.6.
Find the probability that T. will be able to enter one of the two specialties mentioned.
10. The figure shows a labyrinth. The spider crawls into the maze at the "Entrance" point. The spider cannot turn around and crawl back. At each fork, the spider chooses a path that has not yet crawled. Considering the choice of the further path as random, determine with what probability the spider will come to the exit.
OPTION 3
1. 60 athletes participate in the gymnastics championship: 14 from Hungary, 25 from Romania, the rest from Bulgaria. The order in which the gymnasts perform is determined by lot. Find the probability that the athlete who competes first is from Bulgaria.
2. Automatic production line for batteries. The probability that a finished battery is defective is 0.02. Before packaging, each battery goes through a control system. The probability that the system will reject a bad battery is 0.97. The probability that the system will mistakenly reject a good battery is 0.02. Find the probability that a randomly selected battery will be rejected.
3. To enter the institute for the specialty " International relationships”, the applicant must score at least 68 points on the exam in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian and a foreign language. To enter the specialty "Sociology", you need to score at least 68 points in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian language and social studies.
The probability that applicant V. will receive at least 68 points in mathematics is 0.7, in Russian - 0.6, in a foreign language - 0.6 and in social studies - 0.7.
Find the probability that B. will be able to enter one of the two specialties mentioned.
4. The figure shows a labyrinth. The spider crawls into the maze at the "Entrance" point. The spider cannot turn around and crawl back. At each fork, the spider chooses a path that has not yet crawled. Considering the choice of the further path as random, determine with what probability the spider will come to the exit.
5. What is the probability that a randomly chosen natural number from 52 to 67 is divisible by 4?
6. On the geometry exam, the student gets one question from the list of exam questions. The probability that this is an inscribed circle question is 0.1. The probability that this is a trigonometry question is 0.35. There are no questions related to these two topics at the same time. Find the probability that the student will get a question on one of these two topics on the exam.
7. Seva, Slava, Anya, Andrey, Misha, Igor, Nadya and Karina cast lots for who to start the game. Find the probability that a boy will start the game.
8. 5 scientists from Spain, 4 from Denmark and 7 from Holland came to the seminar. The order of reports is determined by a draw. Find the probability that the report of a scientist from Denmark will be the twelfth.
9. There are only 25 tickets in the collection of tickets on philosophy, 8 of them contain a question on Pythagoras. Find the probability that a student will not get a question on Pythagoras in a ticket randomly selected at the exam.
10. There are two payment machines in the store. Each of them can be faulty with a probability of 0.09, regardless of the other automaton. Find the probability that at least one automaton is serviceable.
OPTION 4
1. Groups perform at the rock festival - one from each of the declared countries. The order of performance is determined by lot. What is the likelihood that a band from the USA will perform after a band from Vietnam and after a band from Sweden? Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
2. The probability that student T. correctly solves more than 8 problems on the history test is 0.58. The probability that T. correctly solves more than 7 problems is 0.64. Find the probability that T. correctly solves exactly 8 problems.
3. The factory produces bags. On average, for every 60 quality bags, there are six bags with hidden defects. Find the probability that the purchased bag will be of high quality. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
4. Sasha had four sweets in his pocket - “Mishka”, “Vzlyotnaya”, “Squirrel” and “Roasting”, as well as the keys to the apartment. Taking out the keys, Sasha accidentally dropped one candy from his pocket. Find the probability that the take-off candy is lost.
5. The figure shows a labyrinth. The spider crawls into the maze at the "Entrance" point. The spider cannot turn around and crawl back. At each fork, the spider chooses a path that has not yet crawled. Considering the choice of the further path as random, determine with what probability the spider will come to the exit.
6. In a random experiment, three dice are thrown. Find the probability of getting 15 points in total. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
7. Biathlete shoots at targets 10 times. The probability of hitting the target with one shot is 0.7. Find the probability that the biathlete hit the targets the first 7 times and missed the last 3. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
8. 5 scientists from Switzerland, 7 from Poland and 2 from Great Britain came to the seminar. The order of reports is determined by a draw. Find the probability that the thirteenth is the report of a scientist from Poland.
9. To enter the institute for the specialty "International Law", the applicant must score at least 68 points on the Unified State Examination in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian language and a foreign language. To enter the specialty "Sociology", you need to score at least 68 points in each of the three subjects - mathematics, Russian language and social studies.
The probability that applicant B. will receive at least 68 points in mathematics is 0.6, in Russian - 0.8, in a foreign language - 0.5 and in social studies - 0.7.
Find the probability that B. will be able to enter one of the two specialties mentioned.
10. There are two identical coffee machines in the mall. The probability that the machine will run out of coffee by the end of the day is 0.25. The probability that both machines will run out of coffee is 0.14. Find the probability that by the end of the day there will be coffee left in both vending machines.
Exercise
Demo option
1. and are independent events. Then the following statement is true: a) they are mutually exclusive events
b) ![]()
G) ![]()
e) ![]()
2. , , - event probabilities , , 0 " style="margin-left:55.05pt;border-collapse:collapse;border:none">
3. Probabilities of events and https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image012_30.gif" width="105" height="28 src=">.gif" width="55" height="24"> There is:
a) 1.25 b) 0.3886 c) 0.25 d) 0.8614
d) there is no correct answer
4. Prove equality using truth tables or show that it is false.
Section 2. Probabilities of combining and crossing events, conditional probability, total probability and Bayesian formulas.
Exercise: Choose the correct answer and mark the corresponding letter in the table.
Demo option
1. Throw two dice at the same time. What is the probability that the sum of the rolled points is not greater than 6?
A) ; b) ; V) ; G) ;
d) there is no correct answer
2. Each letter of the word "CRAFT" is written on a separate card, then the cards are mixed. We take out three cards at random. What is the probability of getting the word "WOOD"?
A) ; b) ; V) ; G) ;
d) there is no correct answer
3. Among the second-year students, 50% never missed classes, 40% missed classes no more than 5 days per semester, and 10% missed classes for 6 or more days. Among the students who did not miss classes, 40% received highest mark, among those who missed no more than 5 days - 30% and among the remaining - 10% received the highest score. The student received the highest score on the exam. Find the probability that he missed classes for more than 6 days.
a) https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image024_14.gif" width="17 height=53" height="53">; c) ; d) ; e) no correct answer
Test on the course of probability theory and mathematical statistics.
Section 3. Discrete random variables and their numerical characteristics.
Exercise: Choose the correct answer and mark the corresponding letter in the table.
Demo option
1 . Discrete random variables X and Y are given by their own laws
distribution
Random variable Z = X+Y. Find Probability ![]()
a) 0.7; b) 0.84; c) 0.65; d) 0.78; d) there is no correct answer
2. X, Y, Z are independent discrete random variables. The X value is distributed according to the binomial law with parameters n=20 and p=0.1. The Y value is distributed according to the geometric law with the parameter p=0.4. The value of Z is distributed according to the Poisson law with the parameter =2. Find the variance of a random variable U= 3X+4Y-2Z
a) 16.4 b) 68.2; c) 97.3; d) 84.2; d) there is no correct answer
3. Two-dimensional random vector (X, Y) is given by the distribution law
event, event ![]() . What is the probability of event A+B?
. What is the probability of event A+B?
a) 0.62; b) 0.44; c) 0.72; d) 0.58; d) there is no correct answer
Test on the course of probability theory and mathematical statistics.
Section 4. Continuous random variables and their numerical characteristics.
Exercise: Choose the correct answer and mark the corresponding letter in the table.
Option demo
1. Independent continuous random variables X and Y are uniformly distributed on the segments: X at https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image032_6.gif" width="32" height="23">.
Random variable Z = 3X +3Y +2. Find D(Z)
a) 47.75; b) 45.75; c) 15.25; d) 17.25; d) there is no correct answer
2 ..gif" width="97" height="23">
a) 0.5; b) 1; c) 0; d) 0.75; d) there is no correct answer
3. A continuous random variable X is given by its probability density https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image036_7.gif" width="99" height="23 src=">.
a) 0.125; b) 0.875; c) 0.625; d) 0.5; d) there is no correct answer
4. Random variable X is normally distributed with parameters 8 and 3. Find
a) 0.212; b) 0.1295; c) 0.3413; d) 0.625; d) there is no correct answer
Test on the course of probability theory and mathematical statistics.
Section 5. Introduction to mathematical statistics.
Exercise: Choose the correct answer and mark the corresponding letter in the table.
Demo option
1. The following mathematical expectation estimates are proposed https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image041_6.gif" width="98" height="22">:
A) https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image043_5.gif" width="205" height="40">
C) https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image045_4.gif" width="205" height="40">
E) 0 "style="margin-left:69.2pt;border-collapse:collapse;border:none">
2. The variance of each measurement in the previous problem is . Then the most efficient of the unbiased estimates obtained in the first problem is the estimate
3. Based on the results of independent observations of a random variable X obeying the Poisson law, construct an estimate of the unknown parameter by the method of moments 425 " style="width:318.65pt;margin-left:154.25pt;border-collapse:collapse; border:none">
a) 2.77; b) 2.90; c) 0.34; d) 0.682; d) there is no correct answer
4. Half-width of the 90% confidence interval constructed to estimate the unknown mathematical expectation of a normally distributed random variable X for sample size n=120, sample mean https://pandia.ru/text/78/195/images/image052_3.gif" width="19 "height="16">=5, yes
a) 0.89; b) 0.49; c) 0.75; d) 0.98; d) there is no correct answer
Validation Matrix - test demo
Section 1 | ||||||
A- | B+ | IN- | G- | D+ |
||
Section 2 | ||||||
Section 3 | ||||||
Section 4 | ||||||
Section 5 | ||||||
TEST #1
Topic: Types of random events, classical definition of probability,
elements of combinatorics.
You are offered 5 test items on the topic types of random events, the classical definition of probability, elements of combinatorics. Among the suggested answers only one is true.
| Exercise | Suggested answers |
|
| If the occurrence of an event A affects the probability value of event B, then about events A And IN they say they... | joint; incompatible; dependent; independent. |
|
| On the garland hang 5 flags of different colors. You can count the number of possible combinations of them using: | the formula for the number of placements; formula for the number of permutations; formula for the number of combinations; |
|
| Among the 100 banknotes received at the cash desk, 8 are counterfeit. The cashier randomly takes out one bill. The probability that this banknote will be accepted at the bank is equal to: | ||
| The 25 seater bus includes 4 passengers. They can take any seat on the bus. The number of ways these people can be placed on the bus is calculated by the formula: | number of permutations; number of combinations; number of placements; |
|
| The dice is thrown once. Dropping the number "4" on the top face is: | certain event; impossible event; random event. |
TEST #2
Topic: Theorems of addition and multiplication of probabilities.
You are offered 5 test tasks on the topic of the theorem of addition and multiplication of probabilities. Among the suggested answers only one is true.
| Exercise | Suggested answers |
|
| An event consisting in the fact that either an event will occur A, or an event IN can be designated: |
A-B; |
|
| Formula P(A+B) = P(A) + P(B), corresponds to the probability addition theorem: | dependent events; independent events; joint events; incompatible events. |
|
| The miss probability for a torpedo boat is . The boat fired 6 shots. The probability that the boat hit the target all 6 times is equal to: | ||
| Probability of joint occurrence of events A And IN stand for: | |
|
| The problem is given: in the first box - 5 white and 3 red balls, in the second - 3 white and 10 red balls. One ball was drawn at random from each box. Determine the probability that both balls are the same color. To solve the problem use: | The theorem of multiplication of probabilities of incompatible events and the theorem of addition of probabilities of independent events. The theorem of addition of probabilities of incompatible events; The theorem of multiplication of probabilities of independent events and the theorem of addition of probabilities of incompatible events; The theorem of multiplication of probabilities of dependent events; |
TEST #3
Topic: Random independent trials according to the Bernoulli scheme.
You are offered 5 test tasks on the topic of random independent tests according to the Bernoulli scheme. Among the suggested answers only one is true.
| Suggested answers |
||
| Given the task: The probability that there is a typo on the page of a student's abstract is 0.03. The abstract consists of 8 pages. Determine the probability that exactly 5 of them are misspelled. | Bernoulli formula; Laplace's local theorem; Laplace's integral theorem; Poisson formula. |
|
| The family plans to have 5 children. If we assume the probability of having a boy is 0.515, then the most probable number of girls in the family is equal to: | ||
| There is a group of 500 people. Find the probability that two people have a birthday on New Year. Assume that the probability of being born on a fixed day is . To solve this problem, use: | Bernoulli formula; Laplace's local theorem; Laplace's integral theorem; Poisson formula. |
|
| To determine the probability that in 300 trials an event A happens at least 40 times, if the probability A in each trial is constant and equal to 0.15, use: | Bernoulli's formula and the addition theorem for the probabilities of incompatible events; Laplace's local theorem; Laplace's integral theorem; Poisson's formula, the addition theorem for the probabilities of incompatible events, the property of the probabilities of opposite events. |
|
| The problem is given: it is known that in some area in September there are 18 rainy days. What is the probability that out of seven days randomly taken in this month, two days will be rainy? To solve this problem, use: | Bernoulli formula; Laplace's local theorem; Laplace's integral theorem; Poisson formula. |
TEST #4
Topic: One-dimensional random variables.
You are offered 5 test tasks on the topic of one-dimensional random variables, their ways of setting and numerical characteristics. Among the suggested answers only one is true.
Tests by discipline"Theory of Probability and Mathematical Statistics"
Option 1
What is the mathematical expectation of the random variable X?
a) 1; b) 2; at 4; d) 2.5; e) 3.5.
| ||||||||||||
| q J | ||||||||||||
What is the mathematical expectation of a random variable  ?
?
a) 0.5; b) 0; c) 0.3; d) 2.2; e) 3.

| Measurement number | ||||||||
| x i |
Determine the unbiased estimate of the variance.
a) 48.5; b) 341.7; c) 12.9; d) 63.42; e) 221.1.
Option 2
a) Bernoulli's formula; b) Laplace's local theorem; c) Laplace's integral theorem; d) Poisson's formula.
The mathematical expectation of a random variable X distributed according to the binomial law is:
a) npq; b) np; c) nq; d) pq.
The Laplace function has the following property: Ф(0)=0.
a) true; b) incorrect.
The correlation coefficient characterizes the degree of tightness of the linear relationship between random variables
a) true; b) incorrect.
The distribution matrix of a system of two discrete random variables (X, Y) is given by the table
| y i x i | |||
What is the variance of the random variable Y.
a) 2; b) 5; c) 3.5; d) 2.56; e) 2.2.
| ||||||||||||
| q J | ||||||||||||
What is the variance of a random variable  ?
?
a) 0.9; b) 0.3; c) 1.15; d) 5.6; e) 0.21.









